Tailored synbiotic powder (functional food) to prevent hyperphosphataemia (kidney disorder)
- PMID: 34389737
- PMCID: PMC8363651
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-95176-3
Tailored synbiotic powder (functional food) to prevent hyperphosphataemia (kidney disorder)
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Tailored synbiotic powder (functional food) to prevent hyperphosphataemia (kidney disorder).Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 13;11(1):18560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98194-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34518620 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
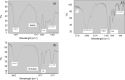
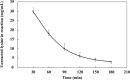
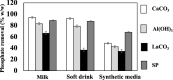
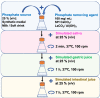
Hyperphosphataemia is treated with phosphate binders, which can cause adverse effects. Spray-dried synbiotic powder (SP) composed of Lactobacillus casei JCM1134 (a phosphate-accumulating organism; PAO) and Aloe vera is potentially a safer alternative for efficient phosphate removal. In this study, a novel strategy was developed; lysine-derivatized deacetylated A. vera (DAVK) was synthesised and fabricated on phosphate-deficient PAO (PDP) for efficient phosphate transfer and then spray-dried with the supernatant of DAV centrifugation to form a sacrificial layer on PDP for SP integrity during gastric passage. In vitro experiments revealed that PAO removed only 1.6% of the phosphate from synthetic media, whereas SP removed 89%, 87%, and 67% (w/v) of the phosphate from milk, soft drink, and synthetic media, respectively, confirming the protective role of A. vera and efficient phosphate transport. Compared with commercial binders, SP effectively removed phosphate from synthetic media, whereas SP and CaCO3 exhibited comparative results for milk and soft drink. Importantly, CaCO3 caused hypercalcaemia. Thus, the described SP presents a promising tool to prevent hyperphosphataemia. This study also revealed a novel factor: diets of patients with chronic kidney disease should be monitored to determine the optimal phosphate binders, as phosphate removal performance depends on the accessible phosphate forms.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jespersen B, et al. Comparison of calcium carbonate and aluminium hydroxide as phosphate binders on biochemical bone markers, PTH(1–84), and bone mineral content in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1991;6:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Peres, L. A., lbert, B., Pércio, P. & Paul, V. Mineral and bone disorder and vascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease. Jornal brasileiro de nefrologia 36, 201–207 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Nagata M, et al. Trends in the prevalence of chronic kidney disease and its risk factors in a general Japanese population: The Hisayama Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010;25:2557–2564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

