Advancing improvement in riverine water quality caused a non-native fish species invasion and native fish fauna recovery
- PMID: 34389739
- PMCID: PMC8363613
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-93751-2
Advancing improvement in riverine water quality caused a non-native fish species invasion and native fish fauna recovery
Abstract
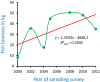
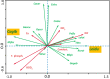
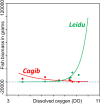
The knowledge of biotic and abiotic drivers that put non-native invasive fishes at a disadvantage to native ones is necessary for suppressing invasions, but the knowledge is scarce, particularly when abiotic changes are fast. In this study, we increased this knowledge by an analysis of the biomass of most harmful Prussian carp Carassius gibelio in a river reviving from biological degradation. The species' invasion followed by the invasion's reversal occurred over only two decades and were documented by frequent monitoring of fish biomass and water quality. An initial moderate improvement in water quality was an environmental filter that enabled Prussian carp's invasion but prevented the expansion of other species. A later substantial improvement stimulated native species' colonization of the river, and made one rheophil, ide Leuciscus idus, a significant Prussian carp's replacer. The redundancy analysis (RDA) of the dependence of changes in the biomass of fish species on water quality factors indicated that Prussian carp and ide responded in a significantly opposite way to changes in water quality in the river over the study period. However, the dependence of Prussian carp biomass on ide biomass, as indicated by regression analysis and analysis of species traits, suggests that the ecomorphological similarity of both species might have produced interference competition that contributed to Prussian carp's decline.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Native freshwater species get out of the way: Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) impacts both fish and benthic invertebrate communities in North America.R Soc Open Sci. 2017 Oct 4;4(10):170400. doi: 10.1098/rsos.170400. eCollection 2017 Oct. R Soc Open Sci. 2017. PMID: 29134062 Free PMC article.
-
Potentially toxic elements in invasive fish species Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) from different freshwater ecosystems and human exposure assessment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Apr;29(19):29152-29164. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17865-w. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34993776
-
Functional diversity measures revealed impacts of non-native species and habitat degradation on species-poor freshwater fish assemblages.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Jun 1;625:861-871. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.316. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29306829
-
Abundance of Opisthorchis felineus Metacercariae in cyprinid fish in the middle Ob River basin (Tomsk region, Russia).Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2021 Feb 5;22:e00113. doi: 10.1016/j.fawpar.2021.e00113. eCollection 2021 Mar. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 33681491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total mercury and methylmercury concentrations in native and invasive fish species in Shadegan International Wetland, Iran, and health risk assessment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Mar;27(7):6765-6773. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07218-z. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31960239 Review.
References
-
- Petsch DK. Causes and consequences of biotic homogenization of freshwater ecosystems. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2016;101:113–122. doi: 10.1002/iroh.201601850. - DOI
-
- Chen GZ, Qiu YP, Li LP. Fish invasions and changes in the fish fauna of the Tarim Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017;37:700–714.
-
- Rau MA, Plavan G, Strungaru SA, Nicoara M, Rodriguez-Lozano P, Mihu-Pintilie A, et al. The impact of amur sleeper (Percottus glenii Dybowsky 1877) on the riverine ecosystem: Food selectivity of amur sleeper in a recently colonized river. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2017;46:96–107. doi: 10.1515/ohs-2017-0010. - DOI
-
- FishBase, Carassius gibelio Bloch 1972, http://fishbase.org (2017).
-
- Olden JD, Comte L, Giam X. Biotic Homogenisation. eLS. Wiley; 2016. pp. 1–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

