Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 recovered individuals
- PMID: 34390647
- PMCID: PMC8332924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109570
Differential effects of the second SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine dose on T cell immunity in naive and COVID-19 recovered individuals
Abstract
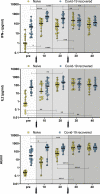
The rapid development of mRNA-based vaccines against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) led to the design of accelerated vaccination schedules that have been extremely effective in naive individuals. While a two-dose immunization regimen with the BNT162b2 vaccine has been demonstrated to provide a 95% efficacy in naive individuals, the effects of the second vaccine dose in individuals who have previously recovered from natural SARS-CoV-2 infection has not been investigated in detail. In this study, we characterize SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific humoral and cellular immunity in naive and previously infected individuals during and after two doses of BNT162b2 vaccination. Our results demonstrate that, while the second dose increases both the humoral and cellular immunity in naive individuals, COVID-19 recovered individuals reach their peak of immunity after the first dose. These results suggests that a second dose, according to the current standard regimen of vaccination, may be not necessary in individuals previously infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: BNT162b2 vaccine; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; T-cell immunity.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.B. declares the filing of a patent application relating to the use of peptide pools in whole blood for detection of SARS-CoV-2 T cells (pending). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Grupper A., Rabinowich L., Schwartz D., Schwartz I.F., Ben-Yehoyada M., Shashar M., Katchman E., Halperin T., Turner D., Goykhman Y. Reduced humoral response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients without prior exposure to the virus. Am. J. Transplant. 2021 doi: 10.1111/ajt.16615. Published online April 18, 2021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kadire S.R., Wachter R.M., Lurie N. Delayed second dose versus standard regimen for Covid-19 vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:e28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

