Adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in recovered severe COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34391981
- PMCID: PMC8349475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104943
Adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in recovered severe COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: There is an imperative need to determine the durability of adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2. We enumerated SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells targeting S1 and M proteins and measured RBD-specific serum IgG over a period of 2-6 months after symptoms onset in a cohort of subjects who had recovered from severe clinical forms of COVID-19.
Patients and methods: We recruited 58 patients (38 males and 20 females; median age, 62.5 years), who had been hospitalized with bilateral pneumonia, 60% with one or more comorbidities. IgG antibodies binding to SARS-CoV-2 RBD were measured by ELISA. SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD69+-expressing-IFNγ-producing-CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were enumerated in heparinized whole blood by flow cytometry for ICS.
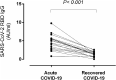
Results: Detectable SARS-CoV-2-S1/M-reactive CD69+-IFN-γ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were displayed in 17 (29.3%) and 6 (10.3%) subjects respectively, at a median of 84 days after onset of symptoms (range, 58-191 days). Concurrent comorbidities increased the risk (OR, 3.15; 95% CI, 1.03-9.61; P = 0.04) of undetectable T-cell responses in models adjusted for age, sex and hospitalization ward. Twenty-one out of the 35 patients (60%) had detectable RBD-specific serum IgGs at a median of 118 days (range, 60-145 days) after symptoms onset. SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific IgG serum levels were found to drop significantly over time.
Conclusion: A relatively limited number of subjects who developed severe forms of COVID-19 had detectable SARS-CoV-2-S1/M IFNγ CD4+ and CD8+ T cells at midterm after clinical diagnosis. Our data also indicated that serum levels of RBD-specific IgGs decline over time, becoming undetectable in some patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Receptor binding domain-specific IgG antibodies; SARS-CoV-2; T cells.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

