Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias
- PMID: 34392353
- PMCID: PMC8497074
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab544
Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias
Abstract
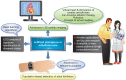
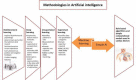
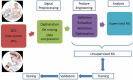
The field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) had adopted simple artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies for decades. Recent renewed interest in deep learning techniques has opened new frontiers in electrocardiography analysis including signature identification of diseased states. Artificial intelligence advances coupled with simultaneous rapid growth in computational power, sensor technology, and availability of web-based platforms have seen the rapid growth of AI-aided applications and big data research. Changing lifestyles with an expansion of the concept of internet of things and advancements in telecommunication technology have opened doors to population-based detection of atrial fibrillation in ways, which were previously unimaginable. Artificial intelligence-aided advances in 3D cardiac imaging heralded the concept of virtual hearts and the simulation of cardiac arrhythmias. Robotics, completely non-invasive ablation therapy, and the concept of extended realities show promise to revolutionize the future of EP. In this review, we discuss the impact of AI and recent technological advances in all aspects of arrhythmia care.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial fibrillation; Electrophysiology; Machine learning; Artificial intelligence.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Turing A. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind 1950;LIX:433–460.
-
- Moore J. The Dartmouth College Artificial Intelligence Conference: the next fifty years. AI Mag 2006;27:87–91.
-
- Marques E, Filho DS, Fernandes FDA, Lacerda C, Soares DA, Seixas L, Augusto A, Sarmet MD, Gismondi RA, Mesquita ET, Mesquita CT. Artificial intelligence in cardiology: concepts, tools and challenges—“the horse is the one who runs, you must be the jockey”. Arq Bras Cardiol 2020;114:718–725. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schläpfer J, Wellens HJ. Computer-interpreted electrocardiograms benefits and limitations. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:1183–1192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

