The EcoCyc Database in 2021
- PMID: 34394059
- PMCID: PMC8357350
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.711077
The EcoCyc Database in 2021
Abstract
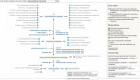
The EcoCyc model-organism database collects and summarizes experimental data for Escherichia coli K-12. EcoCyc is regularly updated by the manual curation of individual database entries, such as genes, proteins, and metabolic pathways, and by the programmatic addition of results from select high-throughput analyses. Updates to the Pathway Tools software that supports EcoCyc and to the web interface that enables user access have continuously improved its usability and expanded its functionality. This article highlights recent improvements to the curated data in the areas of metabolism, transport, DNA repair, and regulation of gene expression. New and revised data analysis and visualization tools include an interactive metabolic network explorer, a circular genome viewer, and various improvements to the speed and usability of existing tools.
Keywords: EcoCyc; Escherichia coli; drug efflux transporters; gene regulation; metabolism; model-organism database.
Copyright © 2021 Keseler, Gama-Castro, Mackie, Billington, Bonavides-Martínez, Caspi, Kothari, Krummenacker, Midford, Muñiz-Rascado, Ong, Paley, Santos-Zavaleta, Subhraveti, Tierrafría, Wolfe, Collado-Vides, Paulsen and Karp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aussel L., Loiseau L., Hajj Chehade M., Pocachard B., Fontecave M., Pierrel F., et al. . (2014). ubiJ, a new gene required for aerobic growth and proliferation in macrophage, is involved in coenzyme Q biosynthesis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 196, 70–79. 10.1128/JB.01065-13, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

