poreCov-An Easy to Use, Fast, and Robust Workflow for SARS-CoV-2 Genome Reconstruction via Nanopore Sequencing
- PMID: 34394197
- PMCID: PMC8355734
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.711437
poreCov-An Easy to Use, Fast, and Robust Workflow for SARS-CoV-2 Genome Reconstruction via Nanopore Sequencing
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: poreCov - An Easy to Use, Fast, and Robust Workflow for SARS CoV-2 Genome Reconstruction via Nanopore Sequencing.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 14;13:875644. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.875644. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35368706 Free PMC article.
Abstract
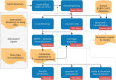
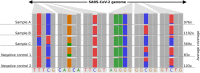
In response to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, a highly increased sequencing effort has been established worldwide to track and trace ongoing viral evolution. Technologies, such as nanopore sequencing via the ARTIC protocol are used to reliably generate genomes from raw sequencing data as a crucial base for molecular surveillance. However, for many labs that perform SARS-CoV-2 sequencing, bioinformatics is still a major bottleneck, especially if hundreds of samples need to be processed in a recurring fashion. Pipelines developed for short-read data cannot be applied to nanopore data. Therefore, specific long-read tools and parameter settings need to be orchestrated to enable accurate genotyping and robust reference-based genome reconstruction of SARS-CoV-2 genomes from nanopore data. Here we present poreCov, a highly parallel workflow written in Nextflow, using containers to wrap all the tools necessary for a routine SARS-CoV-2 sequencing lab into one program. The ease of installation, combined with concise summary reports that clearly highlight all relevant information, enables rapid and reliable analysis of hundreds of SARS-CoV-2 raw sequence data sets or genomes. poreCov is freely available on GitHub under the GNUv3 license: github.com/replikation/poreCov.
Keywords: Nextflow; SARS-CoV-2; bioinformatics; coronavirus – COVID-19; docker; lineages; nanopore sequencing; pipeline.
Copyright © 2021 Brandt, Krautwurst, Spott, Lohde, Jundzill, Marquet and Hölzer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brandt C., Spott R., Hölzer M., Kühnert D., Fuchs S., Lohde M., et al. (2021). Molecular epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 - a regional to global perspective. medRxiv [Preprint]. 10.1101/2021.01.25.21250447 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

