Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation with Bedside Ultrasonography in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Validation Study
- PMID: 34395035
- PMCID: PMC8354344
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1715484
Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation with Bedside Ultrasonography in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Validation Study
Abstract
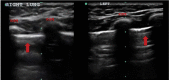
Critically ill patients who are intubated undergo multiple chest X-rays (CXRs) to determine endotracheal tube position; however, other modalities can save time, medical expenses, and radiation exposure. In this article, we evaluated the validity and interrater reliability of ultrasound to confirm endotracheal tube (ETT) position in patients. A prospective study was performed on intubated patients with cuffed ETTs. The accuracy of ultrasound to confirm correct ETT placement in 92 patients was 97.8%. Sensitivity, positive predictive value, and agreement of 97.7, 93.3, and 91.3% were found on comparing ultrasound to CXR findings. Ultrasound is feasible, reliable, and has good interrater reliability in assessing correct ETT position in children.
Keywords: endotracheal intubation; radiation; ultrasound.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Quasney M W, Goodman D M, Billow M. Routine chest radiographs in pediatric intensive care units. Pediatrics. 2001;107(02):241–248. - PubMed
-
- Dincer Y, Sezgin Z. Medical radiation exposure and human carcinogenesis-genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Biomed Environ Sci. 2014;27(09):718–728. - PubMed
-
- DeBoer S, Seaver M, Arndt K. Verification of endotracheal tube placement: a comparison of confirmation techniques and devices. J Emerg Nurs. 2003;29(05):444–450. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources