Network analysis of miRNA targeting m6A-related genes in patients with esophageal cancer
- PMID: 34395102
- PMCID: PMC8325912
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11893
Network analysis of miRNA targeting m6A-related genes in patients with esophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: We investigated the miRNA-m6A related gene network and identified a miRNA-based prognostic signature in patients with esophageal cancer using integrated genomic analysis.
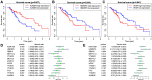
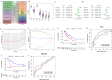
Methods: We obtained expression data for m6A-related genes and miRNAs from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Survival analysis was conducted to identify potential prognostic biomarkers. LASSO Cox regression was performed to construct the overall survival (OS) associated prediction signature. We used the Kaplan-Meier (K-M) curve and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves to explore the signature's efficiency and accuracy. Interactions between the m6A-related genes and miRNAs were identified in starBase3.0 and used to construct the miRNA-m6A related gene network.
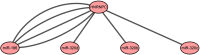
Results: We found that HNRNPC, YTHDF, ZC3H13, YTHDC2, and METTL14 were dysregulated in esophageal cancer tissues. Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that HNRNPC may be an independent risk factor for OS. Five hundred twenty-two potential upstream miRNAs were obtained from starBase3.0. Four miRNAs (miR-186, miR-320c, miR-320d, and miR-320b) were used to construct a prognostic signature, which could serve as a prognostic predictor independent from routine clinicopathological features. Finally, we constructed a key miRNA-m6A related gene network and used one m6A-related gene and four miRNAs associated with the prognosis. The results of our bioinformatics analysis were successfully validated in the human esophageal carcinoma cell lines KYSE30 and TE-1.
Conclusion: Our study identified a 4-miRNA prognostic signature and established a key miRNA-m6A related gene network. These tools may reliably assist with esophageal cancer patient prognosis.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer; HNRNPC; N6-methyladenosine; Overall survival; Prognosis.
© 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Analysis of PD-L1 Expression, Immune Infiltrates, and m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:669750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669750. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054840 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an m6A-Related lncRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis in Patients With Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 26;11:663263. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.663263. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34123820 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of an m6A RNA Methylation Regulators-Based Prognostic Signature for Esophageal Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jul 6;12:5385-5394. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S254870. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32753956 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Status And Prognostic Value Of M6A-associated Genes in Gastric Cancer.J Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;11(10):3027-3040. doi: 10.7150/jca.40866. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32226518 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of N6-methyladenosine methylation-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Front Surg. 2023 Mar 3;10:1052100. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1052100. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36936652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A target microRNAs in serum for cancer detection.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 20;20(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01477-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34930277 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of m6A modification of non-coding RNA in gastrointestinal cancers: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 30;11:1264552. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1264552. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37965577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of main RNA modifications in cancer: N6-methyladenosine, 5-methylcytosine, and pseudouridine.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Apr 28;7(1):142. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01003-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35484099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research on RNA modification in disease diagnosis and prognostic biomarkers: current status and challenges.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Jul 2;26(4):bbaf361. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf361. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40698864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The implications of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in esophageal carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8691-8703. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08575-2. Epub 2023 Aug 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang ZW, Jia YX, Zhang WJ, Song LJ, Gao M, Li MJ, Zhao RH, Li J, Zhong YL, Sun QZ, Qin YR. LncRNA-TUSC7/miR-224 affected chemotherapy resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by competitively regulating DESC1. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2018;37(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0724-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Zhou H, Wu C, Yan H. Identification of miRNA profiling in prediction of tumor recurrence and progress and bioinformatics analysis for patients with primary esophageal cancer: Study based on TCGA database. Pathology Research and Practice. 2018;214(12):2081–2086. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.10.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen JL, Lin ZX, Qin YS, She YQ, Chen Y, Chen C, Qiu GD, Zheng JT, Chen ZL, Zhang SY. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA LINC01419 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its relation to the sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil by mediating GSTP1 methylation. Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology. 2019;11:1758835919838958. doi: 10.1177/1758835919838958. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

