Artificial Inoculation of Epichloë festucae into Lolium perenne, and Visualisation of Endophytic and Epiphyllous Fungal Growth
- PMID: 34395789
- PMCID: PMC8328605
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2990
Artificial Inoculation of Epichloë festucae into Lolium perenne, and Visualisation of Endophytic and Epiphyllous Fungal Growth
Abstract
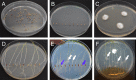
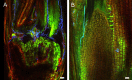
Natural hosts for the fungal endophyte Epichloë festucae include Festuca rubra (fine fescue) and Festuca trachyphylla (hard fescue). Some strains also form stable associations with Lolium perenne (perennial ryegrass). L. perenne is a suitable host to study fungal endophyte-grass interactions, such as endophytic fungal growth within the plant and epiphyllous growth on the plant surface. Here we provide a detailed protocol based on work by, for artificial inoculation of E. festucae into L. perenne, and newly developed staining and visualization techniques for observing endophytic and epiphyllous hyphae and the expressorium, an appressorium-like structure used by the fungus to exit the plant. The staining method uses a combination of glucan binding aniline blue diammonium salt (AB) and chitin binding wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated Alexa Fluor®488 -(WGA-AF488). This protocol will be a useful tool to study Epichloë-grass interactions, particularly the comparison of different Epichloë-grass associations, various endophyte-host developmental stages, as well as the analysis of mutant Epichloë strains.
Keywords: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy; Epichloë; Epiphyllous Growth; Expressorium; Fungal endophyte; Inoculation.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures





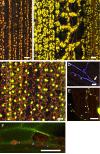
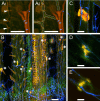
References
-
- Figueroa-Lopez A. M., Cordero-Ramirez J. D., Quiroz-Figueroa F. R. and Maldonado-Mendoza I. E.(2014). A high-throughput screening assay to identify bacterial antagonists against Fusarium verticillioides . J Basic Microbiol 54 Suppl 1: S125-133. - PubMed
-
- Florea S., Schardl C. L. and Hollin W.(2015). Detection and isolation of Epichloë species, fungal endophytes of grasses . Curr Protoc Microbiol 38: 19.A 11 11-19A 11 24. - PubMed
-
- Latch G. C. M. and Christensen M. J.(1985). Artificial infection of grasses with endophytes. Ann Appl Biol 107(1): 17-24.
-
- Scott B., Becker Y., Becker M. and Cartwright G.(2012). Morphogenesis, growth, and development of the grass symbiont Epichlöe festucae. In: Martín, J. P. and Pietro, A. D.(Eds.). Morphogenesis and Pathogenicity in Fungi. Springer, 243-264.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

