Tolerance and Efficacy of Polyethylene Glycol 4000 in Elderly Patients with Chronic Constipation: A Retrospective, Single-center, Observational Study
- PMID: 34395942
- PMCID: PMC8321590
- DOI: 10.23922/jarc.2020-104
Tolerance and Efficacy of Polyethylene Glycol 4000 in Elderly Patients with Chronic Constipation: A Retrospective, Single-center, Observational Study
Abstract
Objectives: This retrospective, observational study aimed to evaluate the tolerance and efficacy of polyethylene glycol 4000 plus electrolytes (PEG 4000) in elderly patients with chronic constipation.
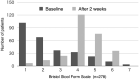
Methods: PEG 4000 powder was orally administered once daily at a dose of one or two 6.9 g sachets as the initial dose. The outcome measures were changes in the Cleveland Clinic Constipation Score (CCCS) and the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS) value before and 2 weeks after drug administration.
Results: This study included 324 patients aged ≥65 years (mean age: 78.6 ± 7.6 years, range: 65-100 years) with chronic constipation. The total CCCS was noted to significantly improve from 11.5 ± 4.6 at baseline to 7.4 ± 5.2 after drug administration. All CCCS sub-scores also improved significantly. The average BSFS value at baseline (2.5 ± 1.6) significantly improved to 4.3 ± 1.1 after treatment. Side effects (16 events) were observed in 13 patients (4.0%), with the most common being diarrhea (6 patients, 1.9%). All events were mild in severity, with none of the symptoms being serious. The cumulative treatment continuation rate at 1 year was 83.1%.
Conclusions: PEG 4000 treatment was safe, effective, and well tolerated in elderly patients with chronic constipation. Thus, it appears to be a promising drug that can be continued for a long time.
Keywords: chronic constipation; elderly; evacuation difficulty; laxatives; polyethylene glycol.
Copyright © 2021 by The Japan Society of Coloproctology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Tatsuya Abe received lecture fees from Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Research Society for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic constipation, the Japanese Society of Gastroenterology. [Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic constipation 2017 ed.]. Nankodo Co, Ltd. 2017. Japanese.
-
- Bharucha AE, Dorn SD, Lembo A, et al. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on constipation. Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan; 144(1): 211-7. - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Hachiro Y, Ohara K, et al. [Current developments in pharmacological therapeutics for chronic constipation]. J Japan Soc Coloproctol. 2019 Nov; 72(10): 600-8. Japanese.
-
- Minguez M, Lopez Higueras A, Judez J. Use of polyethylene glycol in functional constipation and fecal impaction. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016 Dec; 108(12): 790-806. - PubMed

