Sensitive extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RNA virus detection using a chelating resin
- PMID: 34396082
- PMCID: PMC8349732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102960
Sensitive extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RNA virus detection using a chelating resin
Abstract
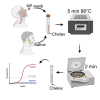
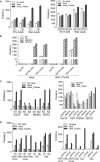
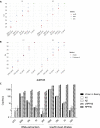
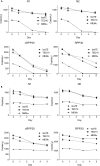
Current conventional detection of SARS-CoV-2 involves collection of a patient's sample with a nasopharyngeal swab, storage of the swab during transport in a viral transport medium, extraction of RNA, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR). We developed a simplified preparation method using a chelating resin, Chelex, which obviates RNA extraction during viral testing. Direct detection RT-qPCR and digital droplet PCR were compared to the current conventional method with RNA extraction for simulated samples and patient specimens. The heat treatment in the presence of Chelex markedly improved detection sensitivity as compared to heat alone, and lack of RNA extraction shortens the overall diagnostic workflow. Furthermore, the initial sample heating step inactivates SARS-CoV-2 infectivity, thus improving workflow safety. This fast RNA preparation and detection method is versatile for a variety of samples, safe for testing personnel, and suitable for standard clinical collection and testing on high-throughput platforms.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Biological sciences research methodologies; Molecular biology experimental approach; Virology.
Conflict of interest statement
NEI (B.G. and R.B.H.) filed an invention disclosure. NEI has protected the intellectual property around this technology which is available for licensing and co-development. Please contact neitechtransfer@nei.nih.gov for more information.
Figures

Update of
-
Sensitive extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RNA virus detection using a novel RNA preparation method.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Feb 1:2021.01.29.21250790. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.29.21250790. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: iScience. 2021 Sep 24;24(9):102960. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102960. PMID: 33532808 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Sensitive extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RNA virus detection using a novel RNA preparation method.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Feb 1:2021.01.29.21250790. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.29.21250790. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: iScience. 2021 Sep 24;24(9):102960. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102960. PMID: 33532808 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by direct RT-qPCR on nasopharyngeal specimens without extraction of viral RNA.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 24;15(7):e0236564. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236564. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32706827 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 detection by rapid RT-qPCR universal for all primary respiratory materials.J Clin Virol. 2020 Sep;130:104579. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104579. Epub 2020 Aug 5. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32795959 Free PMC article.
-
Automated SARS-COV-2 RNA extraction from patient nasopharyngeal samples using a modified DNA extraction kit for high throughput testing.Ann Saudi Med. 2020 Sep-Oct;40(5):373-381. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2020.373. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Ann Saudi Med. 2020. PMID: 32954791 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid processing of SARS-CoV-2 containing specimens for direct RT-PCR.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 10;16(2):e0246867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246867. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33566873 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A point-of-care SARS-CoV-2 test based on reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification without RNA extraction with diagnostic performance same as RT-PCR.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Apr 1;1200:339590. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339590. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35256137 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the AdvanSure One-Stop COVID-19 Plus Kit for SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using a Streamlined RNA Extraction Method.Ann Lab Med. 2023 Sep 1;43(5):508-511. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.508. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Ann Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 37080753 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Release of Nucleic Acids of African Swine Fever Virus and Influenza A Virus from FTA Cards.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 29;22(23):12915. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312915. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884719 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Nucleic Acid Extraction for Aquatic Animal DNA Virus Determination Using Chelex 100 Resin via Conventional PCR and Digital Droplet PCR Detection.Animals (Basel). 2022 Aug 8;12(15):1999. doi: 10.3390/ani12151999. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35953988 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies That Facilitate Extraction-Free SARS-CoV-2 Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests.Viruses. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):1311. doi: 10.3390/v14061311. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35746782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alcoba-Florez J., Gonzalez-Montelongo R., Inigo-Campos A., de Artola D.G., Gil-Campesino H., The Microbiology Technical Support, T., Ciuffreda L., Valenzuela-Fernandez A., Flores C. Fast SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-qPCR in preheated nasopharyngeal swab samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;97:66–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beltrán-Pavez C., Márquez C.L., Muñoz G., Valiente-Echeverría F., Gaggero A., Soto-Rifo R., Barriga G.P. SARS-CoV-2 detection from nasopharyngeal swab samples without RNA extraction. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.03.28.013508. - DOI
-
- Bruce E.A., Huang M.L., Perchetti G.A., Tighe S., Laaguiby P., Hoffman J.J., Gerrard D.L., Nalla A.K., Wei Y., Greninger A.L. Direct RT-qPCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient nasopharyngeal swabs without an RNA extraction step. PLoS Biol. 2020;18:e3000896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

