Ly6chi Infiltrating Macrophages Promote Cyst Progression in Injured Conditional Ift88 Mice
- PMID: 34396149
- PMCID: PMC8359900
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000882021
Ly6chi Infiltrating Macrophages Promote Cyst Progression in Injured Conditional Ift88 Mice
Abstract
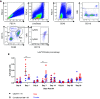
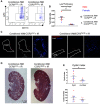
Ly6chi infiltrating macrophage numbers are increased in injured, conditional Ift88 mice, compared with controls.
Loss of Ly6chi infiltrating macrophages slows injury-accelerated cystic disease.
Ly6chi infiltrating macrophages drive cystic disease in non-Pkd1–deficient cystic models.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Mrug reports having consultancy agreements with Chinook, Goldilocks Therapeutics, Natera, Otsuka Corporation, and Sanofi; receiving research funding from Chinook, Goldilocks Therapeutics, Otsuka Corporation, and Sanofi; receiving honoraria from Chinook, Natera, Otsuka Corporations, and Sanofi; and serving as a scientific advisor for—or member of—the PKD Foundation, on the Sanofi STAGED-PKD Steering Committee, and on the advisory board for Santa Barbara Nutrients. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Zimmerman KA, Bentley MR, Lever JM, Li Z, Crossman DK, Song CJ, Liu S, Crowley MR, George JF, Mrug M, Yoder BK: Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies candidate renal resident macrophage gene expression signatures across species. J Am Soc Nephrol 30: 767–781, 2019. 10.1681/ASN.2018090931 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

