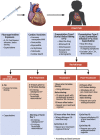
How to Diagnose and Manage Patients With Fluoropyrimidine-Induced Chest Pain: A Single Center Approach
- PMID: 34396276
- PMCID: PMC8352252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2020.06.012
How to Diagnose and Manage Patients With Fluoropyrimidine-Induced Chest Pain: A Single Center Approach
Keywords: 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; CAD, coronary artery disease; CTA, computed tomography angiogram; CV, cardiovascular; FLOX, bolus dosing 5 fluorouracil, leucovirin, oxaliplatin; FOLFOX, continuous infusion 5 fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin; cardiotoxicity; coronary vasospasm; fluoropyrimidine.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

