Effect of community-based nutritional counseling intervention on children's eating habits
- PMID: 34397687
- PMCID: PMC8322548
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026563
Effect of community-based nutritional counseling intervention on children's eating habits
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to assess the outcome of community-based nutritional counseling interventions on eating habits of rural-dwelling children.
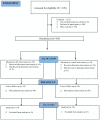
Methods: A group-randomized trial design was used in this study. A total of 108 rural-dwelling children from a community in the Enugu North agricultural zone, Enugu State, who participated in the study. The children were randomly assigned to 2 groups: the treatment group (n = 54) and the no-treatment control group (n = 54). The child eating behavior questionnaire was used for data collection. Parents of the participating children within each study group completed the child eating behavior questionnaire at 3 time points. The data collected were analyzed using an independent sample t test at a probability level of .05.
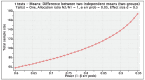
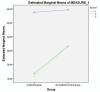
Result: The outcome of the study showed that the children's eating habits in the treatment group improved positively following the community-based nutritional counseling intervention. The positive gain from exposure to the community-based nutritional counseling intervention program was sustained during follow-up for children in the treatment group compared with the no-treatment group.
Conclusion: The community-based nutrition counseling intervention carried out among children in rural communities had a positive adjustment in children's eating habits. The intervention requires the constant collaboration of professional childhood educators, caregivers, home economists, school staff, healthcare specialists, families, and the children themselves. Furthermore, there is a need for future long-term evaluations of the effects of community-based nutritional counseling interventions on children's nutrition and eating habits.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kollataj W, Sygit K, Sygit M, Karwat ID, Kollataj B. Eating habits of children and adolescents from rural regions depending on gender, education, and economic status of parents. Ann Agric Environ Med 2011;18:393–7. - PubMed
-
- Saronga NJ, Mosha IH, Kessy AT, et al. . I eat two meals per day” impact of climate variability on eating habits among households in Rufiji district, Tanzania: a qualitative study. Agric Food Secur 2016;5:14.doi:10.1186/s40066-016-0064-6.
-
- Cahyani AD, Ispurwanto W, Rumeser JA, Setyorini A. Eating Habit Among Workers in Jakarta. 2016;Indonesia: Bina Nusantara University, Published online.
-
- Kramer CV, Allen S. Malnutrition in developing countries. Paediatr Child Health 2015;25:422–7.
-
- Demographic NN. Health Survey 2008. Abuja National Population Commission and ICF Macro 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

