Genomic biomarkers in chronic beryllium disease and sarcoidosis
- PMID: 34399367
- PMCID: PMC8490480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106390
Genomic biomarkers in chronic beryllium disease and sarcoidosis
Abstract
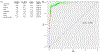
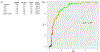
Background Previous gene expression studies have identified genes IFNγ, TNFα, RNase 3, CXCL9, and CD55 as potential biomarkers for sarcoidosis and/or chronic beryllium disease (CBD). We hypothesized that differential expression of these genes could function as diagnostic biomarkers for sarcoidosis and CBD, and prognostic biomarkers for sarcoidosis. Study Design/Methods We performed RT-qPCR on whole blood samples from CBD (n = 132), beryllium sensitized (BeS) (n = 109), and sarcoidosis (n = 99) cases and non-diseased controls (n = 97) to determine differential expression of target genes. We then performed logistic regression modeling and generated ROC curves to determine which genes could most accurately differentiate: 1) CBD versus sarcoidosis 2) CBD versus BeS 3) sarcoidosis versus controls 4) non-progressive versus progressive sarcoidosis. Results CD55 and TNFα were significantly upregulated, while CXCL9 was significantly downregulated in CBD compared to sarcoidosis (p < 0.05). The ROC curve from the logistic regression model demonstrated high discriminatory ability of the combination of CD55, TNFα, and CXCL9 to distinguish between CBD and sarcoidosis with an AUC of 0.98. CD55 and TNFα were significantly downregulated in sarcoidosis compared to controls (p < 0.05). The ROC curve from the model showed a reasonable discriminatory ability of CD55 and TNFα to distinguish between sarcoidosis and controls with an AUC of 0.86. There was no combination of genes that could accurately differentiate between CBD and BeS or sarcoidosis phenotypes. Interpretation CD55, TNFα and CXCL9 expression levels can accurately differentiate between CBD and sarcoidosis, while CD55 and TNFα expression levels can accurately differentiate sarcoidosis and controls.
Keywords: Chronic beryllium disease; Gene expression; Genomic biomarkers; Granulomatous lung disease; Sarcoidosis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Summary Declaration of Interest Statements
Dr. Yang reports consultant fees from Eleven P15, outside the submitted work.
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures:
Dr. Ivana V. Yang reports consultant fees from Eleven P15, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Crouser ED, Maier LA, Wilson KC, Bonham CA, Morgenthau AS, Patterson KC, Abston E, Bernstein RC, Blankstein R, Chen ES, Culver DA, Drake W, Drent M, Gerke AK, Ghobrial M, Govender P, Hamzeh N, James WE, Judson MA, Kellermeyer L, Knight S, Koth LL, Poletti V, Raman SV, Tukey MH, Westney GE, Baughman RP, Diagnosis and Detection of Sarcoidosis. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 201 (2020) e26–e51. https://doi.org/10-1164/rccm.202002-0251ST. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balmes JR, Abraham JL, Dweik RA, Fireman E, Fontenot AP, Maier LA, Muller-Quernheim J, Ostiguy G, Pepper LD, Saltini C, Schuler CR, Takaro TK, Wambach PF, An official American Thoracic Society statement: Diagnosis and management of beryllium sensitivity and chronic beryllium disease, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 190 (2014) e34–e59. https://doi.org/10-1164/rccm.201409-1722ST. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

