Vasopressin infusion in COVID-19 critical illness is not associated with impaired viral clearance: a pilot study
- PMID: 34399981
- PMCID: PMC8289704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.07.005
Vasopressin infusion in COVID-19 critical illness is not associated with impaired viral clearance: a pilot study
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; arginine vasopressin; vasopressor; viraemia.
Figures
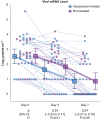
Comment on
-
Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system.Cell. 2021 Apr 15;184(8):2212-2228.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33713620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guérin C., Reignier J., Richard J.C., et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2159–2168. - PubMed
-
- Russell J.A., Walley K.R., Singer J., et al. Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Currigan D.A., Hughes R.J., Wright C.E., Angus J.A., Soeding P.F. Vasoconstrictor responses to vasopressor agents in human pulmonary and radial arteries: an in vitro study. Anesthesiology. 2014;121:930–936. - PubMed
-
- Sarkar J., Golden P.J., Kajiura L.N., Murata L.A., Uyehara C.F. Vasopressin decreases pulmonary-to-systemic vascular resistance ratio in a porcine model of severe hemorrhagic shock. Shock. 2015;43:475–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

