Maintenance of conditioned place avoidance induced by gastric malaise requires NMDA activity within the ventral hippocampus
- PMID: 34400528
- PMCID: PMC8372560
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.052720.120
Maintenance of conditioned place avoidance induced by gastric malaise requires NMDA activity within the ventral hippocampus
Abstract
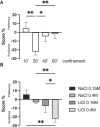
It has been reported that during chemotherapy treatment, some patients can experience nausea before pharmacological administration, suggesting that contextual stimuli are associated with the nauseating effects. There are attempts to reproduce with animal models the conditions under which this phenomenon is observed to provide a useful paradigm for studying contextual aversion learning and the brain structures involved. This manuscript assessed the hippocampus involvement in acquiring and maintaining long-term conditioned place avoidance (CPA) induced by a gastric malaise-inducing agent, LiCl. Our results demonstrate that a reliable induction of CPA is possible after one acquisition trial. However, CPA establishment requires a 20-min confinement in the compartment associated with LiCl administration. Interestingly, both hippocampal regions seem to be necessary for CPA establishment; nonetheless, inactivation of the ventral hippocampus results in a reversion of avoidance and turns it into preference. Moreover, we demonstrate that activation of dorsal/ventral hippocampal NMDA receptors after CS-US association is required for long-term CPA memory maintenance.
© 2021 Hernández-Matias et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures




References
-
- Cloutier CJ, Kavaliers M, Ossenkopp K-P. 2018. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced sickness in adolescent female rats alters the acute-phase response and lithium chloride (LiCl)- induced impairment of conditioned place avoidance/aversion learning, following a homotypic LPS challenge in adulthood. Behav Brain Res 351: 121–130. 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.05.033 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
