This is a preprint.
Broad-spectrum in vitro antiviral activity of ODBG-P-RVn: an orally-available, lipid-modified monophosphate prodrug of remdesivir parent nucleoside (GS-441524)
- PMID: 34401879
- PMCID: PMC8366795
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.08.06.455494
Broad-spectrum in vitro antiviral activity of ODBG-P-RVn: an orally-available, lipid-modified monophosphate prodrug of remdesivir parent nucleoside (GS-441524)
Update in
-
Broad-Spectrum In Vitro Antiviral Activity of ODBG-P-RVn: An Orally-Available, Lipid-Modified Monophosphate Prodrug of Remdesivir Parent Nucleoside (GS-441524).Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0153721. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01537-21. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34817209 Free PMC article.
Abstract
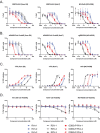
The intravenous administration of remdesivir for COVID-19 confines its utility to hospitalized patients. We evaluated the broad-spectrum antiviral activity of ODBG-P-RVn, an orally available, lipid-modified monophosphate prodrug of the remdesivir parent nucleoside (GS-441524) against viruses that cause diseases of human public health concern, including SARS-CoV-2. ODBG-P-RVn showed 20-fold greater antiviral activity than GS-441524 and had near-equivalent activity to remdesivir in primary-like human small airway epithelial cells. Our results warrant investigation of ODBG-P-RVn efficacy in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, Ray AS, Mackman RL, Soloveva V, Siegel D, Perron M, Bannister R, Hui HC, Larson N, Strickley R, Wells J, Stuthman KS, Van Tongeren SA, Garza NL, Donnelly G, Shurtleff AC, Retterer CJ, Gharaibeh D, Zamani R, Kenny T, Eaton BP, Grimes E, Welch LS, Gomba L, Wilhelmsen CL, Nichols DK, Nuss JE, Nagle ER, Kugelman JR, Palacios G, Doerffler E, Neville S, Carra E, Clarke MO, Zhang L, Lew W, Ross B, Wang Q, Chun K, Wolfe L, Babusis D, Park Y, Stray KM, Trancheva I, Feng JY, Barauskas O, Xu Y, Wong P, et al.2016. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 531:381–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lo MK, Jordan R, Arvey A, Sudhamsu J, Shrivastava-Ranjan P, Hotard AL, Flint M, McMullan LK, Siegel D, Clarke MO, Mackman RL, Hui HC, Perron M, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Nichol ST, Spiropoulou CF. 2017. GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses. Sci Rep 7:43395. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Graham RL, Menachery VD, Gralinski LE, Case JB, Leist SR, Pyrc K, Feng JY, Trantcheva I, Bannister R, Park Y, Babusis D, Clarke MO, Mackman RL, Spahn JE, Palmiotti CA, Siegel D, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Jordan R, Denison MR, Baric RS. 2017. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci Transl Med 9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
