This is a preprint.
Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial
- PMID: 34401888
- PMCID: PMC8366808
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.08.09.21261290
Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial
Update in
-
Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial.Science. 2022 Jan 7;375(6576):43-50. doi: 10.1126/science.abm3425. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Science. 2022. PMID: 34812653 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: In the Coronavirus Efficacy (COVE) trial, estimated mRNA-1273 vaccine efficacy against coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) was 94%. SARS-CoV-2 antibody measurements were assessed as correlates of COVID-19 risk and as correlates of protection.
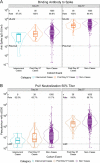
Methods: Through case-cohort sampling, participants were selected for measurement of four serum antibody markers at Day 1 (first dose), Day 29 (second dose), and Day 57: IgG binding antibodies (bAbs) to Spike, bAbs to Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD), and 50% and 80% inhibitory dilution pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titers calibrated to the WHO International Standard (cID50 and cID80). Participants with no evidence of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection were included. Cox regression assessed in vaccine recipients the association of each Day 29 or 57 serologic marker with COVID-19 through 126 or 100 days of follow-up, respectively, adjusting for risk factors.
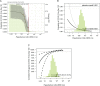
Results: Day 57 Spike IgG, RBD IgG, cID50, and cID80 neutralization levels were each inversely correlated with risk of COVID-19: hazard ratios 0.66 (95% CI 0.50, 0.88; p=0.005); 0.57 (0.40, 0.82; p=0.002); 0.42 (0.27, 0.65; p<0.001); 0.35 (0.20, 0.61; p<0.001) per 10-fold increase in marker level, respectively, multiplicity adjusted P-values 0.003-0.010. Results were similar for Day 29 markers (multiplicity adjusted P-values <0.001-0.003). For vaccine recipients with Day 57 reciprocal cID50 neutralization titers that were undetectable (<2.42), 100, or 1000, respectively, cumulative incidence of COVID-19 through 100 days post Day 57 was 0.030 (0.010, 0.093), 0.0056 (0.0039, 0.0080), and 0.0023 (0.0013, 0.0036). For vaccine recipients at these titer levels, respectively, vaccine efficacy was 50.8% (-51.2, 83.0%), 90.7% (86.7, 93.6%), and 96.1% (94.0, 97.8%). Causal mediation analysis estimated that the proportion of vaccine efficacy mediated through Day 29 cID50 titer was 68.5% (58.5, 78.4%).
Conclusions: Binding and neutralizing antibodies correlated with COVID-19 risk and vaccine efficacy and likely have utility in predicting mRNA-1273 vaccine efficacy against COVID-19.
Trial registration number: COVE ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04470427.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination. CDC COVID-19 Science Briefs. National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Division of Viral Diseases. Atlanta (GA). [Updated 2021 May 27]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570435/. 2021. - PubMed
-
- McGill COVID19 Vaccine Tracker Team. COVID19 Vaccine Tracker. https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/ Access date 21 Jun, 2021. Last updated 19 Jun, 2021. 2021.
-
- Creech CB, Walker SC, Samuels RJ. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. JAMA 2021;325:1318–20. - PubMed
-
- Weller C. Four reasons why we need multiple vaccines for Covid-19. Wellcome Opinion. 6 Jun 2021. Access date 21 Jun 2021. https://wellcome.org/news/four-reasons-why-we-need-multiplevaccines-covi....
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
