Dual mechanisms of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the inspiratory rhythm-generating network
- PMID: 34402425
- PMCID: PMC8390004
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67523
Dual mechanisms of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the inspiratory rhythm-generating network
Abstract
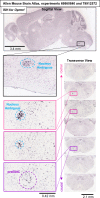
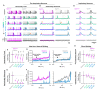
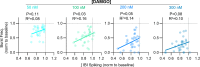
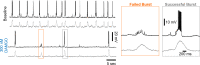
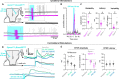
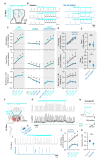
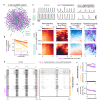
The analgesic utility of opioid-based drugs is limited by the life-threatening risk of respiratory depression. Opioid-induced respiratory depression (OIRD), mediated by the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), is characterized by a pronounced decrease in the frequency and regularity of the inspiratory rhythm, which originates from the medullary preBötzinger Complex (preBötC). To unravel the cellular- and network-level consequences of MOR activation in the preBötC, MOR-expressing neurons were optogenetically identified and manipulated in transgenic mice in vitro and in vivo. Based on these results, a model of OIRD was developed in silico. We conclude that hyperpolarization of MOR-expressing preBötC neurons alone does not phenocopy OIRD. Instead, the effects of MOR activation are twofold: (1) pre-inspiratory spiking is reduced and (2) excitatory synaptic transmission is suppressed, thereby disrupting network-driven rhythmogenesis. These dual mechanisms of opioid action act synergistically to make the normally robust inspiratory rhythm-generating network particularly prone to collapse when challenged with exogenous opioids.
Keywords: Oprm1; breathing; mouse; neuroscience; opioid; pre-bӧtzinger complex; respiratory depression; rhythm-generation.
© 2021, Baertsch et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NB, NB, NB, JR No competing interests declared
Figures









References
-
- Algera MH, Kamp J, van der Schrier R, van Velzen M, Niesters M, Aarts L, Dahan A, Olofsen E. Opioid-induced respiratory depression in humans: a review of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of reversal. British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2019;122:e168–e179. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.12.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

