Coffea arabica bean extract inhibits glucose transport and disaccharidase activity in Caco-2 cells
- PMID: 34405045
- PMCID: PMC8329997
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2021.1449
Coffea arabica bean extract inhibits glucose transport and disaccharidase activity in Caco-2 cells
Abstract
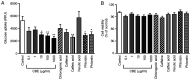
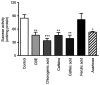
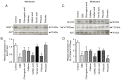
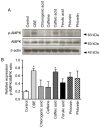
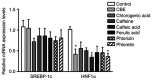
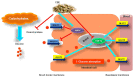
The major constituents of Coffea arabica (coffee), including caffeine, chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid, exhibit antihyperglycemic properties in in vitro and in vivo models. However, whether Coffea arabica bean extract (CBE) regulates glucose uptake activity and the underlying mechanisms involved remain unclear. The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of CBE on glucose absorption and identify the mechanisms involved using an in vitro model. The uptake of a fluorescent glucose analog into Caco-2 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells was determined. The expression levels of sodium glucose co-transporter 1 (SGLT1) and glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) were evaluated. In addition, glycoside hydrolase enzyme activity was investigated. It was observed that CBE inhibited disaccharidase enzyme activity. Furthermore, CBE exerted an inhibitory effect on intestinal glucose absorption by downregulating SGLT1- and GLUT2-mediated 5' AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and suppressing hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α expression. These data suggest that CBE may attenuate glucose absorption and may have potentially beneficial antihyperglycemic effects in the body; however, the mechanisms underlying the effects of CBE must be elucidated through further investigation.
Keywords: 5' AMP-activated protein kinase; CBE; GLUT2; SGLT1; glucose uptake; hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α.
Copyright: © Ontawong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
