Randomized Phase III Trial Evaluating Radiation Following Surgical Excision for Good-Risk Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Long-Term Report From NRG Oncology/RTOG 9804
- PMID: 34406870
- PMCID: PMC8577682
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.01083
Randomized Phase III Trial Evaluating Radiation Following Surgical Excision for Good-Risk Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Long-Term Report From NRG Oncology/RTOG 9804
Abstract
Purpose: To our knowledge, NRG/RTOG 9804 is the only randomized trial to assess the impact of whole breast irradiation (radiation therapy [RT]) versus observation (OBS) in women with good-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), following lumpectomy. Long-term results focusing on ipsilateral breast recurrence (IBR), the primary outcome, are presented here.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients underwent lumpectomy for DCIS that was mammogram detected, size ≤ 2.5 cm, final margins ≥ 3 mm, and low or intermediate nuclear grade. Consented patients were randomly assigned to RT or OBS. Tamoxifen use was optional. Cumulative incidence was used to estimate IBR, log-rank test and Gray's test to compare treatments, and Fine-Gray regression for hazard ratios (HRs).
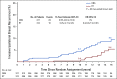
Results: A total of six hundred thirty-six women were randomly assigned from 1999 to 2006. Median age was 58 years and mean pathologic DCIS size was 0.60 cm. Intention to use tamoxifen was balanced between arms (69%); however, actual receipt of tamoxifen varied, 58% RT versus 66% OBS (P = .05). At 13.9 years' median follow-up, the 15-year cumulative incidence of IBR was 7.1% (95% CI, 4.0 to 11.5) with RT versus 15.1% (95% CI, 10.8 to 20.2) OBS (P = .0007; HR = 0.36; 95% CI, 0.20 to 0.66); and for invasive LR was 5.4% (95% CI, 2.7 to 9.5) RT versus 9.5% (95% CI, 6.0 to 13.9) OBS (P = .027; HR = 0.44; 95% CI, 0.21 to 0.91). On multivariable analysis, only RT (HR = 0.34; 95% CI, 0.19 to 0.64; P = .0007) and tamoxifen use (HR = 0.45; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.78; P = .0047) were associated with reduced IBR.
Conclusion: RT significantly reduced all and invasive IBR for good-risk DCIS with durable results at 15 years. These results are not an absolute indication for RT but rather should inform shared patient-physician treatment decisions about ipsilateral breast risk reduction in the long term following lumpectomy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00003857.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
DCIS Update: Escalation or De-escalation? Boost, Fractionation, and Omission of Radiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Mar 15;115(4):813-816. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.11.010. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 36822780 No abstract available.
References
-
- Desantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, et al. Breast cancer statistics 2019 CA Cancer J Clin 69438–4512019 - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Lumpectomy and radiation therapy for the treatment of intraductal breast cancer: Findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-17 J Clin Oncol 16441–4521998 - PubMed
-
- Julien J, Bijker N, Fentimen I, et al. Radio-therapy in breast conserving treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ: First results of the EORTC randomized phase III trial 10853-EORTC Breast Cancer Cooperatie Group and EORTC Radiotherapy Group Lancet 355528–5332000 - PubMed
-
- Emdin S, Granstrand B, Ringberg A, et al. SweDCIS: Radiotherapy after sector resection for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast—Results of a randomized trial in a population offered mammography screening Acta Oncol 45536–5432006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

