25-Hydroxycholesterol protecting from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the inhibition of STING activity
- PMID: 34406977
- PMCID: PMC8436919
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203337
25-Hydroxycholesterol protecting from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the inhibition of STING activity
Abstract
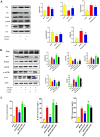
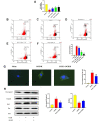
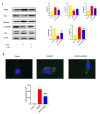
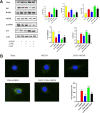
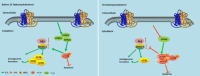
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) injury refers to impaired blood supply to the brain that is caused by a cerebrovascular disease, resulting in local brain tissue ischemia, hypoxic necrosis, and rapid neurological impairment. Nevertheless, the mechanisms involved are unclear, and pharmacological interventions are lacking. 25-Hydroxycholesterol (25-HC) was reported to be involved in cholesterol and lipid metabolism as an oxysterol molecule. This study aimed to determine whether 25-HC exerts a cerebral protective effect on MCAO injury and investigate its potential mechanism. 25-HC was administered prior to reperfusion in a mouse model of MCAO injury. 25-HC evidently decreased infarct size induced by MCAO and enhanced brain function. It reduced stimulator of interferon gene (STING) activity and regulated mTOR to inhibit autophagy and induce cerebral ischemia tolerance. Thus, 25-HC improved MCAO injury through the STING channel. As indicated in this preliminary study, 25-HC improved MCAO injury by inhibiting STING activity and autophagy as well as by reducing brain nerve cell apoptosis. Thus, it is a potential treatment drug for brain injury.
Keywords: 25-hydroxycholesterol; STING; autophagy; mTOR; middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A combination of four active compounds alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in correlation with inhibition of autophagy and modulation of AMPK/mTOR and JNK pathways.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Oct;92(10):1295-306. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23400. Epub 2014 May 7. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 24801159
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Curcumin Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Via Mediating Autophagy and Inflammation.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Jan;64(1):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-1006-x. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29243061
-
Mechanism of ameliorating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by antioxidant inhibition of autophagy based on network pharmacology and experimental verification.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 25;16(8):7474-7486. doi: 10.18632/aging.205773. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38669115 Free PMC article.
-
The CD40/CD40L system regulates rat cerebral microvasculature after focal ischemia/reperfusion via the mTOR/S6K signaling pathway.Neurol Res. 2018 Sep;40(9):717-723. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1473075. Epub 2018 May 29. Neurol Res. 2018. PMID: 29843579
-
Shengmai injection attenuates the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induced autophagy via modulation of the AMPK, mTOR and JNK pathways.Pharm Biol. 2016 Oct;54(10):2288-97. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2016.1155625. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 26983890
Cited by
-
Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on cerebral circulation time in severe carotid artery stenosis: Results from the RIC-CCT trial.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Nov 19;5(11):101796. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101796. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39471820 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
RHBDF2 governs microglial neuroinflammation during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and is positively regulated by the m6A reader YTHDF1.Mol Med. 2025 Sep 2;31(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01326-y. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40898058 Free PMC article.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol as a Signaling Molecule of the Nervous System.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022 Jun;87(6):524-537. doi: 10.1134/S0006297922060049. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022. PMID: 35790411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The STING Signaling: A Novel Target for Central Nervous System Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr 7;45(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01550-4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40195137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol as a negative regulator of diaphragm muscle contractions via estrogen receptor and Ca2+ -dependent pathway.Histochem Cell Biol. 2025 Apr 3;163(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s00418-025-02370-9. Histochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40178695
References
-
- Luo F, Wu L, Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Liu Z, Guo B, Li N, Ju J, Zhou Q, Li S, Yang X, Mak S, Han Y, et al.. The dual-functional memantine nitrate MN-08 alleviates cerebral vasospasm and brain injury in experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage models. Br J Pharmacol. 2019; 176:3318–35. 10.1111/bph.14763 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwamm LH, Wu O, Song SS, Latour LL, Ford AL, Hsia AW, Muzikansky A, Betensky RA, Yoo AJ, Lev MH, Boulouis G, Lauer A, Cougo P, et al., and MR WITNESS Investigators. Intravenous thrombolysis in unwitnessed stroke onset: MR WITNESS trial results. Ann Neurol. 2018; 83:980–93. 10.1002/ana.25235 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

