Mechanisms and Review of Clinical Evidence of Variations in Relative Biological Effectiveness in Proton Therapy
- PMID: 34407443
- PMCID: PMC8688199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.08.015
Mechanisms and Review of Clinical Evidence of Variations in Relative Biological Effectiveness in Proton Therapy
Abstract
Proton therapy is increasingly being used as a radiation therapy modality. There is uncertainty about the biological effectiveness of protons relative to photon therapies as it depends on several physical and biological parameters. Radiation oncology currently applies a constant and generic value for the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of 1.1, which was chosen conservatively to ensure tumor coverage. The use of a constant value has been challenged particularly when considering normal tissue constraints. Potential variations in RBE have been assessed in several published reviews but have mostly focused on data from clonogenic cell survival experiments with unclear relevance for clinical proton therapy. The goal of this review is to put in vitro findings in relation to clinical observations. Relevant in vivo pathways determining RBE for tumors and normal tissues are outlined, including not only damage to tumor cells and parenchyma but also vascular damage and immune response. Furthermore, the current clinical evidence of varying RBE is reviewed. The assessment can serve as guidance for treatment planning, personalized dose prescriptions, and outcome analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest. The sole author was responsible for literature review, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript. He takes full responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Data Availability Statement for this Work
Research data are stored in an institutional repository and will be shared upon request to the corresponding author.
Figures
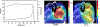
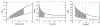



References
-
- McMahon SJ. The linear quadratic model: Usage, interpretation and challenges. Phys Med Biol 2018;64:01TR01. - PubMed
-
- Kalholm F, Grzanka L, Traneus E, Bassler N. A systematic review on the usage of averaged LET in radiation biology for particle therapy. Radiother Oncol 2021;161:211–221. - PubMed
-
- Rørvik E, Fjæra LF, Dahle TJ, et al. Exploration and application of phenomenological RBE models for proton therapy. Phys Med Biol 2018;63 185013. - PubMed
-
- Giedzinski E, Rola R, Fike JR, Limoli CL. Efficient production of reactive oxygen species in neural precursor cells after exposure to 250 MeV protons. Radiat Res 2005;164(Pt 2):540–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

