Upregulation of C/EBPα Inhibits Suppressive Activity of Myeloid Cells and Potentiates Antitumor Response in Mice and Patients with Cancer
- PMID: 34407972
- PMCID: PMC8756351
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0986
Upregulation of C/EBPα Inhibits Suppressive Activity of Myeloid Cells and Potentiates Antitumor Response in Mice and Patients with Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the mechanisms of how therapeutic upregulation of the transcription factor, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPα), prevents tumor progression in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and in different mouse tumor models.
Experimental design: We conducted a phase I trial in 36 patients with HCC (NCT02716012) who received sorafenib as part of their standard care, and were given therapeutic C/EBPα small activating RNA (saRNA; MTL-CEBPA) as either neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment. In the preclinical setting, the effects of MTL-CEBPA were assessed in several mouse models, including BNL-1ME liver cancer, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC), and colon adenocarcinoma (MC38).
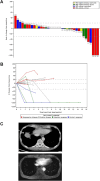
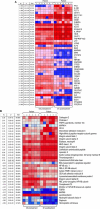
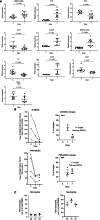
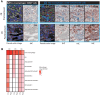
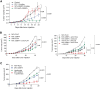
Results: MTL-CEBPA treatment caused radiologic regression of tumors in 26.7% of HCC patients with an underlying viral etiology with 3 complete responders. MTL-CEBPA treatment in those patients caused a marked decrease in peripheral blood monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell (M-MDSC) numbers and an overall reduction in the numbers of protumoral M2 tumor-associated macrophages (TAM). Gene and protein analysis of patient leukocytes following treatment showed CEBPA activation affected regulation of factors involved in immune-suppressive activity. To corroborate this observation, treatment of all the mouse tumor models with MTL-CEBPA led to a reversal in the suppressive activity of M-MDSCs and TAMs, but not polymorphonuclear MDSCs (PMN-MDSC). The antitumor effects of MTL-CEBPA in these tumor models showed dependency on T cells. This was accentuated when MTL-CEBPA was combined with checkpoint inhibitors or with PMN-MDSC-targeted immunotherapy.
Conclusions: This report demonstrates that therapeutic upregulation of the transcription factor C/EBPα causes inactivation of immune-suppressive myeloid cells with potent antitumor responses across different tumor models and in cancer patients. MTL-CEBPA is currently being investigated in combination with pembrolizumab in a phase I/Ib multicenter clinical study (NCT04105335).
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Newman JR, Keating AE. Comprehensive identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays. Science 2003;300:2097–101. - PubMed
-
- Avellino R, Delwel R. Expression and regulation of C/EBPalpha in normal myelopoiesis and in malignant transformation. Blood 2017;129:2083–91. - PubMed
-
- Lourenco AR, Coffer PJ. A tumor suppressor role for C/EBPalpha in solid tumors: more than fat and blood. Oncogene 2017;36:5221–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

