Characterization of Virus Replication, Pathogenesis, and Cytokine Responses in Syrian Hamsters Inoculated with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34408462
- PMCID: PMC8366787
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S323026
Characterization of Virus Replication, Pathogenesis, and Cytokine Responses in Syrian Hamsters Inoculated with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel coronavirus which caused a global respiratory disease pandemic beginning in December 2019. Understanding the pathogenesis of infection and the immune responses in a SARS-CoV-2-infected animal model is urgently needed for vaccine development.
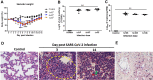
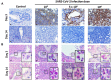
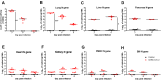
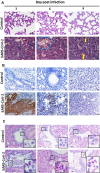
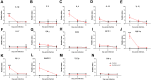
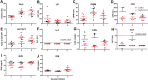
Methods: Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) were intranasally inoculated with 105, 5×105, and 106 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 per animal and studied for up to 14 days. Body weight, viral load and real-time PCR amplification of the SARS-CoV-2 N gene were measured. On days 3, 6 and 9, lung, blood, liver, pancreas, heart, kidney, and bone marrow were harvested and processed for pathology, viral load, and cytokine expression.
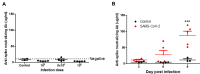
Results: Body weight loss, increased viral load, immune cell infiltration, upregulated cytokine expression, viral RNA, SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein, and mucus were detected in the lungs, particularly on day 3 post-infection. Extremely high expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines MIP-1 and RANTES was detected in lung tissue, as was high expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, and PD-L1. The glutamic oxalacetic transaminase/glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GOT/GPT) ratio in blood was significantly increased at 6 days post-infection, and plasma amylase and lipase levels were also elevated in infected hamsters.
Conclusion: Our results provide new information on immunological cytokines and biological parameters related to the pathogenesis and immune response profile in the Syrian hamster model of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; hamster; immune response; pathogenesis.
© 2021 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dynamic Changes of the Blood Chemistry in Syrian Hamsters Post-Acute COVID-19.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0236221. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02362-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196799 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical symptoms and signs in hamsters during experimental infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus (Coronaviridae: Betacoronavirus)].Vopr Virusol. 2023 Dec 26;68(6):513-525. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-202. Vopr Virusol. 2023. PMID: 38156567 Russian.
-
Detached epithelial cell plugs from the upper respiratory tract favour distal lung injury in Golden Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) when experimentally infected with the A.2 Brazilian SARS-CoV-2 strain.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024 Oct 21;119:e240100. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760240100. eCollection 2024. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2024. PMID: 39442103 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in golden hamsters.Nature. 2020 Jul;583(7818):834-838. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2342-5. Epub 2020 May 14. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32408338 Free PMC article.
-
Hamsters as a Model of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.Comp Med. 2021 Oct 1;71(5):398-410. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-21-000036. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Comp Med. 2021. PMID: 34588095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
After the virus has cleared-Can preclinical models be employed for Long COVID research?PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 7;18(9):e1010741. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010741. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36070309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Live Attenuated COVID-19 Candidate Vaccine for Children: Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Challenge in Hamsters.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;11(2):255. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020255. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851133 Free PMC article.
-
Furin and TMPRSS2 Resistant Spike Induces Robust Humoral and Cellular Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2 Lethal Infection.Front Immunol. 2022 May 2;13:872047. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.872047. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35585971 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces inflammatory bone loss in golden Syrian hamsters.Nat Commun. 2022 May 9;13(1):2539. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30195-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35534483 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Molecular Mechanism of Viral Inhibition of Aerosolized Smart Nano-Enabled Antiviral Therapeutic (SNAT) on SARS-CoV-2-Infected Hamsters.Toxics. 2024 Jul 5;12(7):495. doi: 10.3390/toxics12070495. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39058147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic; 2020. - PubMed
-
- Chan JF-W, Zhang AJ, Yuan S, et al. Simulation of the clinical and pathological manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in golden Syrian hamster model: implications for disease pathogenesis and transmissibility. Clin Infect Dis. 2020:ciaa325. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

