Comparison of Public Health Containment Measures of COVID-19 in China and India
- PMID: 34408516
- PMCID: PMC8367213
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S326775
Comparison of Public Health Containment Measures of COVID-19 in China and India
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to make a comparative analysis of the public health containment measures between China and India, explore the causes of the serious COVID-19 epidemic in India, and eventually to improve global infectious disease control.
Methods: We extracted publicly available data from official websites, summarized the containment measures implemented in China and India, and assessed their effectiveness.
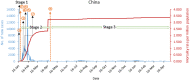
Results: China has responded to the COVID-19 outbreak with strict public health containment measures, including lockdown of Wuhan city, active case tracing, and large-scale testing, ultimately preventing a large increase in daily new cases and maintaining a low mortality rate per million population (as of May 5, 2021, daily new cases were 11 and mortality rate per million population was 3.37). India, although imposing a national lockdown to control the pandemic, has not implemented strict testing, tracking, and quarantine measures due to the overburdened healthcare system. Combined with massive lockdown, it has accelerated human mobility and exacerbated the epidemic, resulting in a rapid increase in daily new cases and a high mortality rate per million population (as of May 5, 2021, daily new cases were 412,431 and mortality rate per million population was 166.79).
Conclusion: China and India implemented public health containment measures to contain the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic based on their national situations. Meanwhile, daily new cases and mortality of COVID-19 also were affected by environmental and socioeconomic. Countries make a comprehensive strategy not only in terms of the biological, pharmaceutical, health, and sanitation sectors but also based on sustainability science and environmental science.
Keywords: COVID-19; China; India; containment measures; public health.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Coccia M. The relation between length of lockdown, numbers of infected people and deaths of Covid-19, and economic growth of countries: lessons learned to cope with future pandemics similar to Covid-19 and to constrain the deterioration of economic system. Sci Total Environ. 2021;775:145801.
-
- COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic. Available from:https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed August4, 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources