Serum galectin-3 and galectin-3 binding protein levels in systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 34408596
- PMCID: PMC8362757
- DOI: 10.5114/ada.2020.92320
Serum galectin-3 and galectin-3 binding protein levels in systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: The roles of galectin-3 (Gal-3) and galectin-3 binding protein (G3BP) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are of ongoing interest, but the data are insufficient due to highly limited available studies. There are no data on cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE).
Aim: To assess serum Gal-3 and G3BP concentrations in SLE patients with and without LE-specific skin lesions, CLE patients and to correlate levels of proteins with clinical and laboratory parameters.
Material and methods: The study included 71 SLE patients with and without LE-specific skin lesions, 23 CLE patients and 40 controls. Gal-3 and G3BP were measured by specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA).
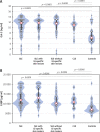
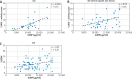
Results: Serum Gal-3 and G3BP concentrations were significantly higher in SLE with and without LE-specific lesions compared to controls, but without differences between SLE groups. Gal-3 and G3BP levels were also elevated in CLE compared to controls (p = 0.001, p = 0.005; respectively). There was a positive correlation between G3BP level and CLASI activity score both in CLE (r = 0.55, p = 0.006) and in SLE patients with LE-specific lesions (r = 0.36, p = 0.02). G3BP and Gal-3 levels did not differ in SLE with LE-specific lesions and CLE. There was a positive correlation between serum G3BP level and the SLEDAI score in SLE patients (r = 0.26, p = 0.03).
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that serum G3BP and Gal-3 are elevated in CLE. Additionally, G3BP might be associated with the extent of skin lesions. There are no differences between G3BP and Gal-3 concentrations in SLE with and without LE-specific skin lesions.
Keywords: galectin-3; galectin-3 binding protein; lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schultz HY, Dutz JP, Furukawa F, et al. From pathogenesis, epidemiology, and genetics to definitions, diagnosis, and treatments of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis: a report from the 3rd International Conference on Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (ICCLE) 2013. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135: 7-12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuhn A, Landmann A. The classification and diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 2014; 48-49: 14-9. - PubMed
-
- Dumic J, Dabelic S, Flogel M. Galectin-3: an open-ended story. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006; 1760: 616-35. - PubMed
-
- Yang RY, Rabinovich GA, Liu FT. Galectins: structure, function and therapeutic potential. Expert Rev Mol Med 2008; 10: e17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
