Real-world implementation of sequential targeted therapies for EGFR-mutated lung cancer
- PMID: 34408792
- PMCID: PMC8366107
- DOI: 10.1177/1758835921996509
Real-world implementation of sequential targeted therapies for EGFR-mutated lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated (EGFR+) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients failing tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) can benefit from next-line targeted therapies, but implementation is challenging.
Methods: EGFR+ NSCLC patients treated with first/second-generation (1G/2G) TKI at our institution with a last follow-up after osimertinib approval (February 2016), were analyzed retrospectively, and the results compared with published data under osimertinib.
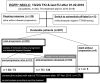
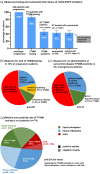
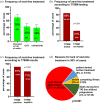
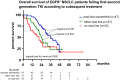
Results: A total of 207 patients received erlotinib (37%), gefitinib (16%) or afatinib (47%). The median age was 66 years, with a predominance of female (70%), never/light-smokers (69%). T790M testing was performed in 174/202 progressive cases (86%), positive in 93/174 (53%), and followed by osimertinib in 87/93 (94%). Among the 135 deceased patients, 94 (70%) received subsequent systemic treatment (43% chemotherapy, 39% osimertinib), while 30% died without, either before (4%) or after progression, due to rapid clinical deterioration (22%), patient refusal of further therapy (2%), or severe competing illness (2%). Lack of subsequent treatment was significantly (4.5x, p < 0.001) associated with lack of T790M testing, whose most frequent cause (in approximately 50% of cases) was also rapid clinical decline. Among the 127 consecutive patients with failure of 1G/2G TKI started after November 2015, 47 (37%) received osimertinib, with a median overall survival of 36 months versus 24 and 21 months for patients with alternative and no subsequent therapies (p = 0.003).
Conclusion: Osimertinib after 1G/2G TKI failure prolongs survival, but approximately 15% and 30% of patients forego molecular retesting and subsequent treatment, respectively, mainly due to rapid clinical deterioration. This is an important remediable obstacle to sequential TKI treatment for EGFR+ NSCLC. It pertains also to other actionable resistance mechanisms emerging under 1G/2G inhibitors or osimertinib, whose rate for lack of next-line therapy is similar (approximately 35% in the FLAURA/AURA3 trials), and highlights the need for closer monitoring alongside broader profiling of TKI-treated EGFR+ NSCLC in the future.
Keywords: EGFR T790M mutation; EGFR+ NSCLC; overall survival; rebiopsy; second line; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: FB reports personal fees from Novartis, MSD, Chugai Pharma, Roche, and AstraZeneca and research grants from AstraZeneca, BMS, and Roche. ALV reports personal fees from AstraZeneca. DK reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb GmbH, personal fees from Pfizer Pharma GmbH, outside the submitted work. FJH reports advisory board fees and honoraria from Lilly, Roche, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Boehringer, Chiesi, Teva, Pulmonx BTG, and Olympus as well as research funding from Lilly, Roche, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Boehringer, Chiesi, and Teva. CPH reports consultation, lecture and other fees from Novartis, Basilea, Bayer, Grifols, Boehringer, Pierre Fabre, Covidien, Siemens, Chiesi, Intermune, MEDA Pharma, Bracco, Pfizer, MSD, Roche, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Schering-Plough, Essex, Gilead, MeVis, Fresenius, and Astellas as well as ownership of GSK stocks TM reports research funding from Roche and patents with Roche. JRF reports advisory board honoraria from Boehringer, Roche, Celgene, and AstraZeneca. PS reports advisory board honoraria from Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, and AstraZeneca as well as speaker’s honoraria and research funding from Roche, AstraZeneca, and Novartis. AS reports advisory board honoraria and/or speaker fees: Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Eli Lilly, Roche, BMS, Illumina, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, and Thermo Fisher, and research grants from BMS, Bayer, and Chugai. MT reports advisory board honoraria from Novartis, Lilly, BMS, MSD, Roche, Celgene, Takeda, AbbVie, Boehringer, speaker’s honoraria from Lilly, MSD, Takeda, research funding from AstraZeneca, BMS, Celgene, Novartis, Roche and travel grants from BMS, MSD, Novartis, Boehringer. PC reports lecture/advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Chugai, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Takeda, as well as research funding from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda.
Figures
References
-
- Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al.. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 2020; 382: 41–50. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Cheng Y, Zhou X, et al.. Improvement in overall survival in a randomized study that compared dacomitinib with gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR-activating mutations. J Clin Oncol 2018; 36: 2244–2250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

