Inhibition of PKC/MEK pathway suppresses β1-integrin and mitigates breast cancer cells proliferation
- PMID: 34408972
- PMCID: PMC8361284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.07.012
Inhibition of PKC/MEK pathway suppresses β1-integrin and mitigates breast cancer cells proliferation
Abstract
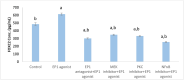
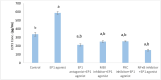
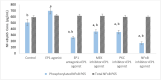
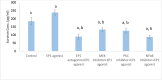
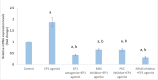
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and β1-integrin have been correlated with breast cancer, where both could enhance progression and metastasis. Protein kinase C (PKC) and MEK have played a vital role in breast cancer development. Our study was conducted to elucidate the effect of inhibition of E-prostanoid receptor 1 (EP1)/ PKC/ MEK/ β1-integrin pathway in mitigating breast cancer progression and to evaluate the role of the intermediate signals FOXC2, E2F1, NF-ҡB and survivin. MCF7 cells were treated with 17 -PT-PGE2, an EP1 agonist, for 24 h, and β1-integrin was measured. To MCF7 cells treated with 17-PT-PGE2, inhibitors of either EP1, MEK, PKC or NF-ҡB were added followed by measurement of β1-integrin gene expression and cell proliferation in each case. Addition of 17- PT-PGE2 to MCF7 cells showed enhancement of both cell proliferation, and cell cycle transition from G1 to S phase. In addition, activation of EP1 receptor increased β1-integrin expression. On the contrary, inhibition of EP1 receptor showed a decrease in the cell proliferation, β1-integrin expression and cells transition to S phase, but increased cell count in apoptotic phase. Selective inhibition of each of MEK, PKC, and NF-ҡB suppressed 17 -PT-PGE2-mediated β1-integrin expression as well as cell proliferation. Furthermore, FOXC2, phosphorylated NF-ҡB, E2F1, and survivin levels were upregulated with 17- PT-PGE2 and suppressed by MEK, PKC and NF-ҡB inhibitors. Targeting the biochemical mediators of PKC/MEK pathway may be of value in developing new chemical entities for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; E2F1; FOXC2; NF-ҡB; Prostaglandin E2; β1-integrin.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ma J., Chen M., Xia S., Shu W., Guo Y., Wang Y., Xu Y., Bai X., Zhang L., Zhang H., Zhang M., Wang Y., Leng J. Prostaglandin E2 promotes liver cancer cell growth by the upregulation of FUSE-binding protein 1 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2013;42(3):1093–1104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

