Case Report: A Novel Heterozygous Mutation of CD2AP in a Chinese Family With Proteinuria Leads to Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 34408996
- PMCID: PMC8365467
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.687455
Case Report: A Novel Heterozygous Mutation of CD2AP in a Chinese Family With Proteinuria Leads to Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
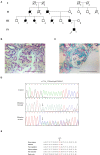
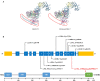
Idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a relatively frequent kidney disorder that manifest clinically as proteinuria and progressive loss of renal function. Genetic factors play a dominant role in the occurrence of FSGS. CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) is an adapter molecule and is essential for the slit-diaphragm assembly and function. Mutations in the CD2AP gene can contribute to FSGS development. Here, we describe a Chinese family of four generations with unexplained proteinuria. The proband, a 12-year-old boy, was diagnosed as FSGS. Whole-exome sequencing (WES) revealed an unknown frameshift insertion mutation (p.K579Efs*7) of CD2AP gene that leads to a truncation of CD2AP protein. Bioinformatics strategies predicted that the novel mutation was pathogenic. The mutation was absent in either healthy family members or our 200 healthy controls. In summary, we used WES to explore the genetic lesion of FSGS patients and identified a novel mutation in CD2AP gene. This work broadens the mutation spectrum of CD2AP gene and provides data for genetic counseling to additional FSGS patients.
Keywords: CD2AP; FSGS; heterozygote; mutation; whole-exome sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Zhang, Luo, Sheng, Wang, Dong, Fan and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fan LL, Liu L, Luo FM, Du R, Wang CY, Dong Y, et al. . A novel heterozygous variant of the COL4A4 gene in a Chinese family with hematuria and proteinuria leads to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and chronic kidney disease. Mol Genet Genomic Med. (2020) 8:e1545. 10.1002/mgg3.1545 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

