Plant Extracts Rich in Polyphenols as Potent Modulators in the Growth of Probiotic and Pathogenic Intestinal Microorganisms
- PMID: 34409062
- PMCID: PMC8366775
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.688843
Plant Extracts Rich in Polyphenols as Potent Modulators in the Growth of Probiotic and Pathogenic Intestinal Microorganisms
Abstract
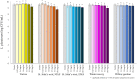
Medicinal plants and their extracts contain substantial quantities of polyphenols. As metabolically active plant metabolites, polyphenols are food components with a wide range of biological activities. Given their poor absorbability in the digestive tract their activity toward the human host is typically mediated through interaction with intestinal microbes. As a result, polyphenols comprise a novel group of prebiotics. In this study, we tested the effect of five polyphenol-rich extracts from four medicinal herbs on the growth of probiotic and pathogenic microbes. The studied medicinal herbs were Gentiana asclepiadea L. (willow gentian), Hypericum perforatum L. (St. John's wort), Satureja montana L. (winter savory), and Achillea millefolium L. (yarrow). All these plants are traditionally used for the treatment of digestive problems. Extracts were prepared using safe solvent combinations. We tested the impact of addition of plant extracts on the growth of three probiotic lactobacilli and probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii. The effect of addition of plant extracts to liquid media (concentration range 0.25-10 mg/mL) on the growth of probiotics, was tested in vitro. The antimicrobial activity of the extracts was tested against several opportunistic bacteria and yeast. St. John's wort, winter savory, and willow gentian extracts showed a stimulative effect on probiotic yeast growth, while the highest growth-stimulating effect was achieved when microwave-assisted yarrow extract was used in the concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. Under these conditions growth of S. boulardii was increased 130-fold. In addition, the yarrow extract stimulated the growth of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v. The growth of two Lacticasibacillus rhamnosus strains was not stimulated by the addition of any extracts. Our results show that plant polyphenol-rich extracts can influence the growth of microorganisms that are typical members of the intestinal microbiota. For the first time we demonstrate that probiotic yeast growth can be stimulated by extracts of medicinal herbs, which when accompanied by suppression of Candida yeasts suggests a potential benefit of the treatment in diseases that are associated with fungal dysbiosis.
Keywords: Achillea millefolium L.; Gentiana asclepiadea L.; Hypericum perforatum L.; Satureja montana L.; antimicrobial activity; medicinal herbs; polyphenols; prebiotics.
Copyright © 2021 Milutinović, Dimitrijević-Branković and Rajilić-Stojanović.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
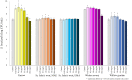


Similar articles
-
Effects of brewing process on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of herbs.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Aug 31;25(4):965-970. doi: 10.1007/s10068-016-0157-9. eCollection 2016. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 30263361 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous ethanolic extract of St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.) induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human malignant cells in vitro.Pharmazie. 2002 May;57(5):323-31. Pharmazie. 2002. PMID: 12061257
-
Levels of some microelements and essential heavy metals in herbal teas in Serbia.Acta Pol Pharm. 2014 May-Jun;71(3):385-91. Acta Pol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25265817
-
Hypericum perforatum (St John's wort) beyond depression: A therapeutic perspective for pain conditions.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:136-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.016. Epub 2017 Feb 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28216196 Review.
-
Understanding drug interactions with St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.): impact of hyperforin content.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;71(1):129-138. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12858. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29411879 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus paracasei HY7015 and Lycopus lucidus Turcz. Extract Promotes Human Dermal Papilla Cell Cytoprotective Effect and Hair Regrowth Rate in C57BL/6 Mice.Molecules. 2022 Nov 25;27(23):8235. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238235. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500327 Free PMC article.
-
Putative Mechanisms Underlying the Beneficial Effects of Polyphenols in Murine Models of Metabolic Disorders in Relation to Gut Microbiota.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Mar 18;44(3):1353-1375. doi: 10.3390/cimb44030091. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Fermentation on Bioactivity and the Composition of Polyphenols Contained in Polyphenol-Rich Foods: A Review.Foods. 2023 Sep 3;12(17):3315. doi: 10.3390/foods12173315. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of essential oils from two salvia species with in vitro and in silico analysis targeting 1AJ6 and 1R4U proteins.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 28;13(1):14038. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41178-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37640782 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Biological Activities of Paederia grandidieri Leaf Extracts.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):12960. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312960. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swidsinski A, Loening-Baucke V, Schulz S, Manowsky J, Verstraelen H, Swidsinski S. Functional anatomy of the colonic bioreactor: impact of antibiotics and Saccharomyces boulardii on bacterial composition in human fecal cylinders. Syst Appl Microbiol. (2016) 39:67–75. 10.1016/j.syapm.2015.11.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hsieh SY, Lian YZ, Lin IH, Yang YC, Tinkov AA, Skalny AV, et al. . Combined Lycium babarum polysaccharides and C-phycocyanin increase gastric Bifidobacterium relative abundance and protect against gastric ulcer caused by aspirin in rats. Nutr Metab. (2021) 18:1–16. 10.1186/s12986-020-00538-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

