Combined iliac crest graft and short-scar pectoralis major flap for clavicular non-union reconstruction
- PMID: 34409127
- PMCID: PMC8366646
- DOI: 10.1080/23320885.2021.1962717
Combined iliac crest graft and short-scar pectoralis major flap for clavicular non-union reconstruction
Abstract
Recently, we reported defect coverage in the clavicular region with a scar-sparing pectoralis major flap. We successfully combine this flap with a clavicular reconstruction by an iliac bone graft for non-union now. We propose this reconstructive combination for cases of clavicular non-union with lack of soft tissue coverage.
Keywords: Reconstructive surgery; head and neck; scar.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
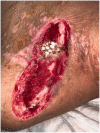
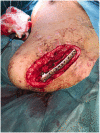



References
-
- Kirchhoff C, Banke IJ, Beirer M, et al. . Operative management of clavicular non-union: iliac crest bone graft and anatomic locking compression plate. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2013;25(5):483–498. - PubMed
-
- Wei F-C, Mardini S.. Flaps and reconstructive surgery. 2nd ed. London: Elsevier; 2016.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
