Proton Reirradiation for Locoregionally Recurrent Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34409209
- PMCID: PMC8361062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2021.100710
Proton Reirradiation for Locoregionally Recurrent Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Local-regional recurrence (LRR) of breast cancer after prior adjuvant radiation (RT) can present a clinical challenge. Proton therapy is recommended by the American Society for Radiation Oncology in cases where reirrradiation is needed; however, data are limited. We present the toxicity and outcomes after reirradiation for local-regional recurrence of breast cancer with proton therapy.
Methods and materials: A single-institution retrospective review identified patients with the following criteria: LRR of breast cancer, prior photon radiation to the same region, proton beam reirradiation, and definitive intent. Surgery or systemic therapy at the time of recurrence was used when indicated. The log-rank test was used to compare Kaplan-Meier survival estimates. Kruskal-Wallis tests were performed to compare worst reported toxicities with clinical variables.
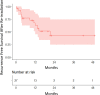
Results: The population included 27 patients with a history of prior radiation and treated with proton therapy for LRR between 2012 and 2019. The median interval between courses was 9.7 years. Proton reirradiation regimens included whole breast/chest wall (WB/CW) with regional nodal RT (22/27), nodal RT alone (2/27), or WB/CW alone (3/27). The median dose was 51 Gy, and the most common fractionation was 1.5 Gy twice daily. Median follow-up after reirradiation was 16.6 months. Acute grade 3 toxicities included dermatitis in 2 patients and breast pain in 2 patients. Grade 2 or higher late toxicities included 6 G2 rib fractures and 1 G2 brachial plexopathy, 1 G3 dermatitis, 1 G3 breast pain, and 1 G4 dermatitis. Twelve patients had new documented recurrences of which 1 was a second in-field LRR, and there were 7 deaths.
Conclusions: Proton salvage reirradiation to median 51 Gy in 1.5 Gy twice daily appears to be safe with acceptable acute and late toxicity, and effective with >95% local-regional control.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Aalders K, van Bommel AC, van Dalen T. Contemporary risks of local and regional recurrence and contralateral breast cancer in patients treated for primary breast cancer. Eur J Can. 2016;63:118–126. - PubMed
-
- McBride A, Allen P, Woodward W. Locoregional recurrence risk for patients with T1,2 breast cancer with 1-3 positive lymph nodes treated with mastectomy and systemic treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;89:392–398. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

