Bilateral Visual Loss Caused by Pneumosinus Dilatans: Idiopathic Cases are not Always Reversible
- PMID: 34409232
- PMCID: PMC8365582
- DOI: 10.4103/2452-2325.288940
Bilateral Visual Loss Caused by Pneumosinus Dilatans: Idiopathic Cases are not Always Reversible
Abstract
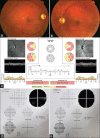
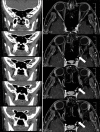
Purpose: To report a rare case of primary pneumosinus dilatans (PSD) and to specify the cardinal imaging findings associated with this condition.
Methods: A 20-year-old patient presented with bilateral profound visual loss as a result of primary PSD. A detailed review of clinical findings and presumed pathophysiological basis of vision loss was performed.
Results: Other than undiagnosed primary hypothyroidism, no other abnormalities were found. With the diagnosis of PSD, the patient underwent optic nerve decompression through transnasal sphenoidotomy. However, after nine months of follow-up, no improvement in the patient's vision was attained.
Conclusion: Unlike previous reports of favorable visual results after sphenoidotomy and bilateral decompression of the optic nerves, vision recovery was not achieved in this case.
Keywords: Optic atrophy; Paranasal sinus; Pneumosinus dilatans.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Current Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ricci JA. Pneumosinus dilatans: Over 100 years without an etiology. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75:1519–26. - PubMed
-
- Desai NS, Saboo SS, Khandelwal A, Ricci JA. Pneumosinus dilatans: Is it more than an aesthetic concern? J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25:418–21. - PubMed
-
- Andrew T, Voglewede JM. Bilateral pneumosinus dilatans of the sphenoid sinuses causing visual loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol Extra. 2015;10:79–83.
-
- Parizel PM, Carpentier K, Van Marck V, Venstermans C, De Belder F, Van Goethem J, et al. Pneumosinus dilatans in anterior skull base meningiomas. Neuroradiology. 2013;55:307–11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
