Impact of facial and truncal acne on quality of life: A multi-country population-based survey
- PMID: 34409378
- PMCID: PMC8362284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.002
Impact of facial and truncal acne on quality of life: A multi-country population-based survey
Abstract
Background: Acne confers an increased risk of physical, psychiatric, and psychosocial sequelae, potentially affecting multiple dimensions of health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Morbidity associated with truncal acne is poorly understood.
Objective: To determine how severity and location of acne lesions impact the HRQoL of those who suffer from it.
Methods: A total of 694 subjects with combined facial and truncal acne (F+T) and 615 with facial acne only (F) participated in an online, international survey. Participants self-graded the severity of their acne at different anatomical locations and completed the dermatology life quality index (DLQI).
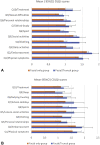
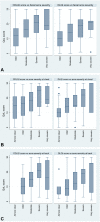
Results: The F+T participants were twice as likely to report "very large" to "extremely large" impact on HRQoL (ie, DLQI > 10 and children's DLQI [CDLQI] > 12) as compared with the F participants (DLQI: odds ratio [OR] 1.61 [95% confidence interval {CI} 1.02-2.54]; CDLQI: OR 1.86 [95% CI 1.10-3.14]). The impact of acne on HRQoL increased with increasing acne severity on the face (DLQI and CDLQI P values = .001 and .017, respectively), chest (P = .003; P = .008), and back (P = .001; P = .028).
Limitations: Temporal evaluation of acne impact was not estimated.
Conclusions: Facial and truncal acne was associated with a greater impact on HRQoL than facial acne alone. Increasing severity of truncal acne increases the adverse impact on HRQoL irrespective of the severity of facial acne.
Keywords: CDLQI, children's dermatology life quality index; CI, confidence interval; CompAQ; CompAQ, Comprehensive Acne Quality of Life; DLQI, dermatology life quality index; F+T, combined facial and truncal acne; F, facial acne only; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; OR, odds ratio; dermatology life quality index (DLQI); facial acne; patient-reported outcomes; quality of life; truncal acne.
© 2021 by the American Academy of Dermatology, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Tan has acted as a consultant for and/or received grants/honoraria from Bausch, 10.13039/501100009754Galderma, 10.13039/100004319Pfizer, Almirall, Boots/10.13039/100005153Walgreens, Botanix, Cipher, 10.13039/501100009754Galderma, Novan, 10.13039/100004336Novartis, Promius, 10.13039/501100004296Sun, Vichy. Dr Chavda is an employee of Galderma. Dr Beissert, Dr Cook-Bolden, Dr Harper, Dr Hebert, Dr Lain, Dr Layton, Dr Weiss, and Pr Dréno have acted as investigators and consultants for Galderma. Dr Rocha has acted as an advisor and/or speaker and received honoraria from Eucerin, Galderma, Johnson&Johnson and Leo Pharm.
Figures
Comment in
-
July 2021: Quality of life and patient-reported outcome measures in dermatology.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Jul;85(1):35. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.04.094. Epub 2021 May 6. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33965464 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin A.R., Lookingbill D.P., Botek A., Light J., Thiboutot D., Girman C.J. Health-related quality of life among patients with facial acne—assessment of a new acne-specific questionnaire. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26(5):380–385. - PubMed
-
- Hay R.J., Johns N.E., Williams H.C. The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(6):1527–1534. - PubMed
-
- Nast A., Dréno B., Bettoli V. European evidence-based (S3) guidelines for the treatment of acne. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26(suppl 1):1–29. - PubMed
-
- Del Rosso J.Q., Bikowski J.B., Baum E. A closer look at truncal acne vulgaris: prevalence, severity, and clinical significance. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6(6):597–600. - PubMed
-
- Gollnick H.P., Finlay A.Y., Shear N. Global Alliance to Improve Outcomes in Acne. Can we define acne as a chronic disease? If so, how and when? Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(5):279–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

