Tilted implantation technique for edentulous patients
- PMID: 34409792
- PMCID: PMC8381128
- DOI: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.04.002
Tilted implantation technique for edentulous patients
Abstract
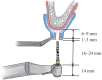
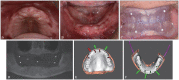
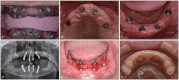
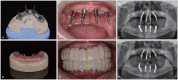
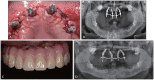
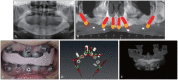
The tilted implantation technique is characterized by placing the implant at an angle of more than 15° and less than 45° from the horizontal plane. This technique can avoid damaging the maxillary sinus, inferior alveolar nerve, nasal base, and other anatomical structures when the height of the upper and lower jaw available bone is insufficient, to maximize the use of available bone and avoid a large range of bone increment. The tilted implantation technique can reduce the trauma of the surgery, increase the possibility of immediate restoration and shorten the treatment cycle, which has been widely used clinically. In this review, the scope of application, design elements, design scheme and complications of the tilted implantation technique for edentulous patients will be described.
倾斜植入技术是指当上、下颌可用骨高度不足时,为避让上颌窦、下牙槽神经、鼻底等解剖结构,采取与水平面呈超过15º、小于45º角度植入种植体,最大限度地利用可用骨,避免大范围骨增量的种植方法。牙列缺失患者常存在骨量不足,倾斜种植技术减小了患者的手术创伤,增加了即刻修复的可能性,缩短了患者的治疗周期,在临床中的应用日益广泛。本文对牙列缺失患者临床常用倾斜种植技术的适用范围、设计要素、设计方案及并发症作以阐述。.
Keywords: bone defect; dental implantation; edentulous; pterygomaxillary implant; tilted implantation.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:作者声明本文无利益冲突。
Figures






References
-
- Brånemark PI, Hansson BO, Adell R, et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period[J] Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Suppl. 1977;16:1–132. - PubMed
-
- Mattsson T, Köndell PA, Gynther GW, et al. Implant treatment without bone grafting in severely resorbed edentulous maxillae[J] J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57(3):281–287. - PubMed
-
- Krekmanov L, Kahn M, Rangert B, et al. Tilting of posterior mandibular and maxillary implants for improved prosthesis support[J] Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15(3):405–414. - PubMed
-
- Fortin Y, Sullivan RM, Rangert BR. The Marius implant bridge: surgical and prosthetic rehabilitation for the completely edentulous upper jaw with moderate to severe resorption: a 5-year retrospective clinical study[J] Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2002;4(2):69–77. - PubMed
-
- Maló P, Rangert B, Nobre M. “All-on-Four” immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous mandibles: a retrospective clinical study[J] Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5(Suppl 1):2–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
