Diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil counts in histopathological tissue analysis in periprosthetic joint infection using the ICM, IDSA, and EBJIS criteria
- PMID: 34409845
- PMCID: PMC8414440
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.108.BJR-2021-0058.R1
Diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil counts in histopathological tissue analysis in periprosthetic joint infection using the ICM, IDSA, and EBJIS criteria
Abstract
Aims: Histology is an established tool in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections (PJIs). Different thresholds, using various infection definitions and histopathological criteria, have been described. This study determined the performance of different thresholds of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (≥ 5 PMN/HPF, ≥ 10 PMN/HPF, ≥ 23 PMN/10 HPF) , when using the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and the International Consensus Meeting (ICM) 2018 criteria for PJI.
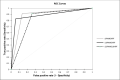
Methods: A total of 119 patients undergoing revision total hip (rTHA) or knee arthroplasty (rTKA) were included. Permanent histology sections of periprosthetic tissue were evaluated under high power (400× magnification) and neutrophils were counted per HPF. The mean neutrophil count in ten HPFs was calculated (PMN/HPF). Based on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and the z-test, thresholds were compared.
Results: Using the EBJIS criteria, a cut-off of ≥ five PMN/HPF showed a sensitivity of 93% (95% confidence interval (CI) 81 to 98) and specificity of 84% (95% CI 74 to 91). The optimal threshold when applying the IDSA and ICM criteria was ≥ ten PMN/HPF with sensitivities of 94% (95% CI 79 to 99) and 90% (95% CI 76 to 97), and specificities of 86% (95% CI 77 to 92) and 92% (95% CI 84 to 97), respectively. In rTKA, a better performance of histopathological analysis was observed in comparison with rTHA when using the IDSA criteria (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: With high accuracy, histopathological analysis can be supported as a confirmatory criterion in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infections. A threshold of ≥ five PMN/HPF can be recommended to distinguish between septic and aseptic loosening, with an increased possibility of detecting more infections caused by low-virulence organisms. However, neutrophil counts between one and five should be considered suggestive of infection and interpreted carefully in conjunction with other diagnostic test methods. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2021;10(8):536-547.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; EBJIS; Histology; Histopathology; Infectious Diseases; Joint Infection; Periprosthetic joint infection; aseptic loosening; diagnostic tests; hips; infections; knee arthroplasty; organisms; periprosthetic joint infections (PJIs); rTKA.
Figures




References
-
- AAOS . Diagnosis and prevention of periprosthetic joint infections: clinical practice guideline. 2019. https://aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/pji/pji-cli... (date last accessed 28 July 2021).
-
- Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. . Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):e1–e25. - PubMed
-
- Shohat N, Bauer T, Buttaro M, et al. . Hip and knee section, what is the definition of a periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) of the knee and the hip? can the same criteria be used for both joints?: proceedings of international consensus on orthopedic infections. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(2S):S325–S327. - PubMed
-
- Banit DM, Kaufer H, Hartford JM. Intraoperative frozen section analysis in revision total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;401:230–238. - PubMed

