Ten simple rules for creating reusable pathway models for computational analysis and visualization
- PMID: 34411100
- PMCID: PMC8375987
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009226
Ten simple rules for creating reusable pathway models for computational analysis and visualization
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
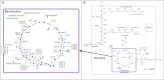
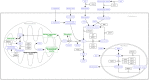
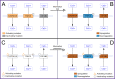
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

