Evaluation of silver nanoparticles for the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health workers: In vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 34411199
- PMCID: PMC8375774
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256401
Evaluation of silver nanoparticles for the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health workers: In vitro and in vivo
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospital areas is of a particular concern, since the close interaction between health care personnel and patients diagnosed with COVID-19, which allows virus to be easily spread between them and subsequently to their families and communities. Preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare personnel is essential to reduce the frequency of infections and outbreaks during the pandemic considering that they work in high-risk areas. In this research, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were tested in vitro and shown to have an inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 infection in cultured cells. Subsequently, we assess the effects of mouthwash and nose rinse with ARGOVIT® silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 contagion in health workers consider as high-risk group of acquiring the infection in the General Tijuana Hospital, Mexico, a hospital for the exclusive recruitment of patients diagnosed with COVID-19. We present a prospective randomized study of 231 participants that was carried out for 9 weeks (during the declaration of a pandemic). The "experimental" group was instructed to do mouthwash and nose rinse with the AgNPs solution; the "control" group was instructed to do mouthwashes and nose rinse in a conventional way. The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was significantly lower in the "experimental" group (two participants of 114, 1.8%) compared to the "control" group (thirty-three participants of 117, 28.2%), with an 84.8% efficiency. We conclude that the mouth and nasal rinse with AgNPs helps in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health personnel who are exposed to patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
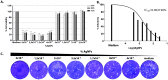
References
-
- World Health Organization. Archived: WHO Timeline—COVID-19. In: Archived: WHO Timeline—COVID-19 [Internet]. [cited 30 Jul 2020]. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline--covid-19?g...
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. In: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. [Internet]. 2020. http://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptoms of Coronavirus. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

