Light-responsive and Protic Ruthenium Compounds Bearing Bathophenanthroline and Dihydroxybipyridine Ligands Achieve Nanomolar Toxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 34411308
- PMCID: PMC8810589
- DOI: 10.1111/php.13508
Light-responsive and Protic Ruthenium Compounds Bearing Bathophenanthroline and Dihydroxybipyridine Ligands Achieve Nanomolar Toxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
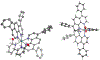
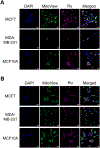
We report new ruthenium complexes bearing the lipophilic bathophenanthroline (BPhen) ligand and dihydroxybipyridine (dhbp) ligands which differ in the placement of the OH groups ([(BPhen)2 Ru(n,n'-dhbp)]Cl2 with n = 6 and 4 in 1A and 2A , respectively). Full characterization data are reported for 1A and 2A and single crystal X-ray diffraction for 1A . Both 1A and 2A are diprotic acids. We have studied 1A , 1B , 2A , and 2B (B = deprotonated forms) by UV-vis spectroscopy and 1 photodissociates, but 2 is light stable. Luminescence studies reveal that the basic forms have lower energy 3 MLCT states relative to the acidic forms. Complexes 1A and 2A produce singlet oxygen with quantum yields of 0.05 and 0.68, respectively, in acetonitrile. Complexes 1 and 2 are both photocytotoxic toward breast cancer cells, with complex 2 showing EC50 light values as low as 0.50 μM with PI values as high as >200 vs. MCF7. Computational studies were used to predict the energies of the 3 MLCT and 3 MC states. An inaccessible 3 MC state for 2B suggests a rationale for why photodissociation does not occur with the 4,4'-dhbp ligand. Low dark toxicity combined with an accessible 3 MLCT state for 1 O2 generation explains the excellent photocytotoxicity of 2.
© 2021 American Society for Photobiology.
Figures

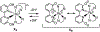


References
-
- Monro S, Colón KL, Yin H, Roque J, Konda P, Gujar S, Thummel RP, Lilge L, Cameron CG and McFarland SA (2019) Transition Metal Complexes and Photodynamic Therapy from a Tumor-Centered Approach: Challenges, Opportunities, and Highlights from the Development of TLD1433. Chem. Rev 119, 797–828. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fong J, Kasimova K, Arenas Y, Kaspler P, Lazic S, Mandel A and Lilge L (2015) A novel class of ruthenium-based photosensitizers effectively kills in vitro cancer cells and in vivo tumors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci 14, 2014–2023. - PubMed
-
- Reichardt C, Sainuddin T, Wächtler M, Monro S, Kupfer S, Guthmuller J, Gräfe S, McFarland S and Dietzek B (2016) Influence of Protonation State on the Excited State Dynamics of a Photobiologically Active Ru(II) Dyad. J. Phys. Chem. A 120, 6379–6388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

