Microbiome reduction prevents lipid accumulation during early diapause in the northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens pipiens
- PMID: 34411585
- PMCID: PMC8530159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2021.104295
Microbiome reduction prevents lipid accumulation during early diapause in the northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens pipiens
Abstract
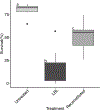
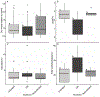
The mosquito microbiome is critical to multiple facets of their biology, including larval development and disease transmission. For mosquitoes that reside in temperate regions, periods of diapause are critical to overwintering survival, but how the microbiome impacts this state is unknown. In this study, we compared the midgut microbial communities of diapausing and non-diapausing Culex pipiens and assessed how a reduced midgut microbiome influences diapause preparation. High community variability was found within and between non-diapausing and diapausing individuals, but no specific diapause-based microbiome was noted. Emergence of adult, diapausing mosquitoes under sterile conditions generated low bacterial load (LBL) lines with nearly a 1000-fold reduction in bacteria levels. This reduction in bacterial content resulted in significantly lower survival of diapausing females after two weeks, indicating acquisition of the microbiome in adult females is critical for survival throughout diapause. LBL diapausing females had high carbohydrate levels, but did not accumulate lipid reserves, suggesting an inability to process ingested sugars necessary for diapause-associated lipid accumulation. Expression patterns of select genes associated with mosquito lipid metabolism during diapause showed no significant differences between LBL and control lines, suggesting transcriptional changes may not underlie impaired lipid accumulation. Overall, a diverse, adult-acquired microbiome is critical for diapause in C. pipiens to process sugar reserves and accumulate lipids that are necessary to survive prolonged overwintering.
Keywords: Culex pipiens; Dormancy; Lipid levels; Metabolism; Microbiome.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

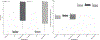
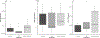
References
-
- Almada AA (2015). Interactions between calanoid copepod hosts and their associated microbiota (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
-
- Benoit JB, & Denlinger DL (2007). Suppression of water loss during adult diapause in the northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens. Journal of experimental biology, 210(2), 217–226. - PubMed
-
- Bercik P, Denou E, Collins J, Jackson W, Lu J, Jury J, ... & Collins SM (2011). The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology, 141(2), 599–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

