An overview of the preclinical discovery and development of remdesivir for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 34412564
- PMCID: PMC8425432
- DOI: 10.1080/17460441.2021.1970743
An overview of the preclinical discovery and development of remdesivir for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
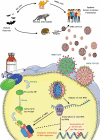
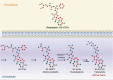
Introduction: Remdesivir (RDV) is an inhibitor of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases that are active in some RNA viruses, including the Ebola virus and zoonotic coronaviruses. When severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was identified as the etiologic agent of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), several investigations have assessed the potential activity of RDV in inhibiting viral replication, giving rise to hope for an effective treatment.
Areas covered: In this review, the authors describe the main investigations leading to the discovery of RDV and its subsequent development as an antiviral agent, focusing on the main clinical trials investigating its efficacy in terms of symptom resolution and mortality reduction.
Expert opinion: RDV is the most widely investigated antiviral drug for the treatment of COVID-19. This attention on RDV activity against SARS-CoV-2 is justified by promising in vitro studies, which demonstrated that RDV was able to suppress viral replication without significant toxicity. Such activity was confirmed by an investigation in an animal model and by the results of preliminary clinical investigations. Nevertheless, the efficacy of RDV in reducing mortality has not been clearly demonstrated.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Dexamethasone; RNA polymerase; Remdesivir.
Figures
References
-
- Nili A, Farbod A, Neishabouri A, et al. Remdesivir: A beacon of hope from Ebola virus disease to COVID-19. Rev Med Virol. 2020;30:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
