X-linked recessive TLR7 deficiency in ~1% of men under 60 years old with life-threatening COVID-19
- PMID: 34413140
- PMCID: PMC8532080
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl4348
X-linked recessive TLR7 deficiency in ~1% of men under 60 years old with life-threatening COVID-19
Abstract
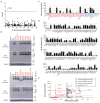
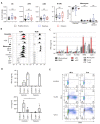
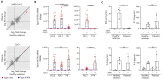
Autosomal inborn errors of type I IFN immunity and autoantibodies against these cytokines underlie at least 10% of critical COVID-19 pneumonia cases. We report very rare, biochemically deleterious X-linked TLR7 variants in 16 unrelated male individuals aged 7 to 71 years (mean: 36.7 years) from a cohort of 1,202 male patients aged 0.5 to 99 years (mean: 52.9 years) with unexplained critical COVID-19 pneumonia. None of the 331 asymptomatically or mildly infected male individuals aged 1.3 to 102 years (mean: 38.7 years) tested carry such TLR7 variants (p = 3.5 × 10-5). The phenotypes of five hemizygous relatives of index cases infected with SARS-CoV-2 include asymptomatic or mild infection (n=2, 5 and 38 years), or moderate (n=1, 5 years), severe (n=1, 27 years), or critical (n=1, 29 years) pneumonia. Two boys (aged 7 and 12 years) from a cohort of 262 male patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia (mean: 51.0 years) are hemizygous for a deleterious TLR7 variant. The cumulative allele frequency for deleterious TLR7 variants in the male general population is < 6.5x10-4 We also show that blood B cell lines and myeloid cell subsets from the patients do not respond to TLR7 stimulation, a phenotype rescued by wild-type TLR7 The patients' blood plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) produce low levels of type I IFNs in response to SARS-CoV-2. Overall, X-linked recessive TLR7 deficiency is a highly penetrant genetic etiology of critical COVID-19 pneumonia, in about 1.8% of male patients below the age of 60 years. Human TLR7 and pDCs are essential for protective type I IFN immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in the respiratory tract.
Copyright © 2021, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

References
-
- Ciancanelli M. J., Huang S. X., Luthra P., Garner H., Itan Y., Volpi S., Lafaille F. G., Trouillet C., Schmolke M., Albrecht R. A., Israelsson E., Lim H. K., Casadio M., Hermesh T., Lorenzo L., Leung L. W., Pedergnana V., Boisson B., Okada S., Picard C., Ringuier B., Troussier F., Chaussabel D., Abel L., Pellier I., Notarangelo L. D., García-Sastre A., Basler C. F., Geissmann F., Zhang S. Y., Snoeck H. W., Casanova J. L., Infectious disease. Life-threatening influenza and impaired interferon amplification in human IRF7 deficiency. Science 348, 448–453 (2015). 10.1126/science.aaa1578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

