Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19
- PMID: 34413211
- PMCID: PMC8433531
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2105815118
Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19
Abstract
The global spread of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and the associated disease COVID-19, requires therapeutic interventions that can be rapidly identified and translated to clinical care. Traditional drug discovery methods have a >90% failure rate and can take 10 to 15 y from target identification to clinical use. In contrast, drug repurposing can significantly accelerate translation. We developed a quantitative high-throughput screen to identify efficacious agents against SARS-CoV-2. From a library of 1,425 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds and clinical candidates, we identified 17 hits that inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection and analyzed their antiviral activity across multiple cell lines, including lymph node carcinoma of the prostate (LNCaP) cells and a physiologically relevant model of alveolar epithelial type 2 cells (iAEC2s). Additionally, we found that inhibitors of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway exacerbate SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Notably, we discovered that lactoferrin, a glycoprotein found in secretory fluids including mammalian milk, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in the nanomolar range in all cell models with multiple modes of action, including blockage of virus attachment to cellular heparan sulfate and enhancement of interferon responses. Given its safety profile, lactoferrin is a readily translatable therapeutic option for the management of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; drug repurposing screening; lactoferrin.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
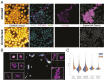

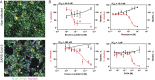
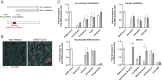

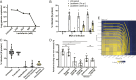

Update of
-
Morphological Cell Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Identifies Drug Repurposing Candidates for COVID-19.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Dec 7:2020.05.27.117184. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.27.117184. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 7;118(36):e2105815118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2105815118. PMID: 32577649 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lin L., et al. ., Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Gut 69, 997–1001 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

