Malaria infection and severe disease risks in Africa
- PMID: 34413238
- PMCID: PMC7611598
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abj0089
Malaria infection and severe disease risks in Africa
Abstract
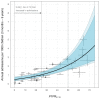
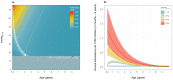
The relationship between community prevalence of Plasmodium falciparum and the burden of severe, life-threatening disease remains poorly defined. To examine the three most common severe malaria phenotypes from catchment populations across East Africa, we assembled a dataset of 6506 hospital admissions for malaria in children aged 3 months to 9 years from 2006 to 2020. Admissions were paired with data from community parasite infection surveys. A Bayesian procedure was used to calibrate uncertainties in exposure (parasite prevalence) and outcomes (severe malaria phenotypes). Each 25% increase in prevalence conferred a doubling of severe malaria admission rates. Severe malaria remains a burden predominantly among young children (3 to 59 months) across a wide range of community prevalence typical of East Africa. This study offers a quantitative framework for linking malaria parasite prevalence and severe disease outcomes in children.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Tracking severe malaria disease.Science. 2021 Aug 20;373(6557):855-856. doi: 10.1126/science.abk3443. Science. 2021. PMID: 34413225 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

