Dendrimers for cancer immunotherapy: Avidity-based drug delivery vehicles for effective anti-tumor immune response
- PMID: 34414690
- PMCID: PMC9485970
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.1752
Dendrimers for cancer immunotherapy: Avidity-based drug delivery vehicles for effective anti-tumor immune response
Abstract
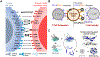
Cancer immunotherapy, or the utilization of a patient's own immune system to treat cancer, has shifted the paradigm of cancer treatment. Despite meaningful responses being observed in multiple studies, currently available immunotherapy platforms have only proven effective to a small subset of patients. To address this, nanoparticles have been utilized as a novel carrier for immunotherapeutic drugs, achieving robust anti-tumor effects with increased adaptive and durable responses. Specifically, dendrimer nanoparticles have attracted a great deal of scientific interest due to their versatility in various therapeutic applications, resulting from their unique physicochemical properties and chemically well-defined architecture. This review offers a comprehensive overview of dendrimer-based immunotherapy technologies, including their formulations, biological functionalities, and therapeutic applications. Common formulations include: (1) modulators of cytokine secretion of immune cells (adjuvants); (2) facilitators of the recognition of tumorous antigens (vaccines); (3) stimulators of immune effectors to selectively attack cells expressing specific antigens (antibodies); and (4) inhibitors of immune-suppressive responses (immune checkpoint inhibitors). On-going works and prospects of dendrimer-based immunotherapies are also discussed. Overall, this review provides a critical overview on rapidly growing dendrimer-based immunotherapy technologies and serves as a guideline for researchers and clinicians who are interested in this field. This article is categorized under: Nanotechnology Approaches to Biology > Nanoscale Systems in Biology Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Discovery > Nanomedicine for Oncologic Disease Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Discovery > Emerging Technologies.
Keywords: dendrimers; drug delivery; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; nanoparticles.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no potential conflict of interest
Figures


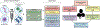
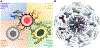
References
-
- Ada G (2003). Overview of Vaccines. In Robinson A, Hudson MJ, & Cranage MP (Eds.), Vaccine Protocols (pp. 1–17). Humana Press. 10.1385/1-59259-399-2:1 - DOI
-
- Ahmad SM, Martinenaite E, Holmström M, Jørgensen MA, Met Ö, Nastasi C, Klausen U, Donia M, Pedersen LM, Munksgaard L, Ødum N, Woetmann A, Svane IM, & Andersen MH (2018). The inhibitory checkpoint, PD-L2, is a target for effector T cells: Novel possibilities for immune therapy. Oncoimmunology, 7(2), e1390641. 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1390641 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aleanizy FS, Alqahtani FY, Seto S, Al Khalil N, Aleshaiwi L, Alghamdi M, Alquadeib B, Alkahtani H, Aldarwesh A, Alqahtani QH, Abdelhady HG, & Alsarra I (2020). Trastuzumab Targeted Neratinib Loaded Poly-Amidoamine Dendrimer Nanocapsules for Breast Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 15, 5433–5443. 10.2147/IJN.S256898 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

