Wearable myoelectric interface enables high-dose, home-based training in severely impaired chronic stroke survivors
- PMID: 34415114
- PMCID: PMC8419406
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51442
Wearable myoelectric interface enables high-dose, home-based training in severely impaired chronic stroke survivors
Abstract
Background: High-intensity occupational therapy can improve arm function after stroke, but many people lack access to such therapy. Home-based therapies could address this need, but they don't typically address abnormal muscle co-activation, an important aspect of arm impairment. An earlier study using lab-based, myoelectric computer interface game training enabled chronic stroke survivors to reduce abnormal co-activation and improve arm function. Here, we assess feasibility of doing this training at home using a novel, wearable, myoelectric interface for neurorehabilitation training (MINT) paradigm.
Objective: Assess tolerability and feasibility of home-based, high-dose MINT therapy in severely impaired chronic stroke survivors.
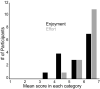
Methods: Twenty-three participants were instructed to train with the MINT and game for 90 min/day, 36 days over 6 weeks. We assessed feasibility using amount of time trained and game performance. We assessed tolerability (enjoyment and effort) using a customized version of the Intrinsic Motivation Inventory at the conclusion of training.
Results: Participants displayed high adherence to near-daily therapy at home (mean of 82 min/day of training; 96% trained at least 60 min/day) and enjoyed the therapy. Training performance improved and co-activation decreased with training. Although a substantial number of participants stopped training, most dropouts were due to reasons unrelated to the training paradigm itself.
Interpretation: Home-based therapy with MINT is feasible and tolerable in severely impaired stroke survivors. This affordable, enjoyable, and mobile health paradigm has potential to improve recovery from stroke in a variety of settings. Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT03401762.
© 2021 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Slutzky reports non‐financial support from Myomo, Inc during the conduct of the study. In addition, Dr. Slutzky has a patent issued related to the MINT device, and has consulted for Battelle on their Strategic Advisory Board.
Figures



References
-
- Cramer SC. Brain repair after stroke. N Engl J Med 2010;362(19):1827–1829. - PubMed
-
- Virani Salim S, Alonso A, Benjamin Emelia J, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020;141(9):e139–e596. - PubMed
-
- Sveen U, Bautz‐Holter E, Margrethe Sodring K, Bruun Wyller T, Laake K. Association between impairments, self‐care ability and social activities 1 year after stroke. Disabil Rehabil 1999;21(8):372–377. - PubMed
-
- Nudo RJ, Wise BM, SiFuentes F, Milliken GW. Neural substrates for the effects of rehabilitative training on motor recovery after ischemic infarct. Science 1996;272(5269):1791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

