Towards a shared understanding of sustainability for neglected tropical disease programs
- PMID: 34415903
- PMCID: PMC8378706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009595
Towards a shared understanding of sustainability for neglected tropical disease programs
Abstract
Background: Sustainability within neglected tropical disease (NTD) programs is a complex and challenging issue. The need for a shared understanding about what sustainability means for NTD programs is more important than ever as stakeholders are currently realigning for the next decade of NTD programming with the launch of WHO's new NTD roadmap for 2012-2030. The aim of this paper is to assess different perspectives to generate a working definition of sustainability for NTD programs.
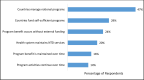
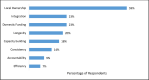
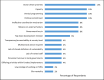
Methodology/principal findings: This study surveyed affiliates of the NTD NGO Network (NNN) about their definitions of sustainability and then analyzed the data using an inductive and deductive process. The research team drafted a sustainability statement based on the survey findings and then solicited and incorporated feedback on the statement from a diverse group of expert reviewers. The final statement includes a working definition of sustainability for NTD programs that highlights three key essential components to sustainability: domestic commitment, responsive resource mobilization, and accountability.
Conclusions/significance: This research resulted in a sustainability statement, based on a survey and extensive consultation with stakeholders, that represents a starting point for shared understanding around the concept of sustainability for NTD programs. Future collaborative work should build off this definition and seek to incorporate indicators for sustainability into programmatic decision-making.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors Influencing the Sustainability of Neglected Tropical Disease Elimination Programs: A Multi-Case Study of the Kenya National Program for Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):1090-1093. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0261. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32124717 Free PMC article.
-
Organization of oversight for integrated control of neglected tropical diseases within Ministries of Health.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Nov 21;12(11):e0006929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006929. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30462639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Tools and Nuanced Interventions to Accelerate Achievement of the 2030 Roadmap for Neglected Tropical Diseases.Clin Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 25;78(Suppl 2):S77-S82. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae070. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38662694 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the factors influencing the motivation of community drug distributors towards the control and elimination of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs).PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Dec 6;11(12):e0006065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006065. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 29211746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations for a sustainability framework for neglected tropical diseases programming.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021 Jan 28;115(2):176-178. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/traa196. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 33508097 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Community intervention programmes with people affected by leprosy: Listening to the voice of professionals.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Mar 28;16(3):e0010335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010335. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 35344566 Free PMC article.
-
Tackling schistosomiasis in fisherfolk communities in Uganda: Enablers and challenges for implementing paediatric schistosomiasis mass drug administration from the perspective of district health authorities.Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2025 Jul;68(7):778-786. doi: 10.1007/s00103-025-04066-w. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2025. PMID: 40478256 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and control of trachoma in the state of Ceará, Northeast Brazil, 2007-2021.Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2023 Jan 23;56:e0207-2022. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0207-2022. eCollection 2023. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2023. PMID: 36700599 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of contextual, setting and implementation factors on a podoconiosis intervention in Rural Ethiopia: Results from a qualitative study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 11;20(7):e0328237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328237. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40644472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation. Geneva; 2012.
-
- World Health Organization. Ending the neglect to attain the Sustainable Development Goals: a sustainability framework for action against neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030 [Internet]. Geneva; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240019027
-
- World Health Organization. Integrating Neglected Tropical Diseases into Global Health and Development: 4th WHO NTDs Report. Geneva; 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources